by Fronetics | Dec 17, 2014 | Big Data, Blog, Data/Analytics, Internet of Things

The Internet of Things (IoT) is ubiquitous. Because of this it can seem abstruse. Puneet Mehta does a great job of putting the concept in layman’s terms: “[A] plethora of “dumb” objects becom[ing] connected, sending signals to each other and alerts to our phones, and creating mounds of “little data” on all of us that will make marketers salivate.”
The mounds of data created by the advent of the IoT does not just make marketers salivate. Gartner predicts that the IoT will add $1.9 trillion in value to the economy by 2020. Looking ahead, Cisco estimates that the IoT will create over $14 trillion in value over the next 10 years.
In 2003 there were 500 million connected devices. Cisco estimates that this number will increase to 50 billion by 2020. Morgan Stanley believes this number will be higher – it estimates there will be 75 billion IoT devices by 2020.
“Dumb” objects are becoming connected; the physical and digital worlds are converging. Mounds of data are being collected.
IoT and Big Data
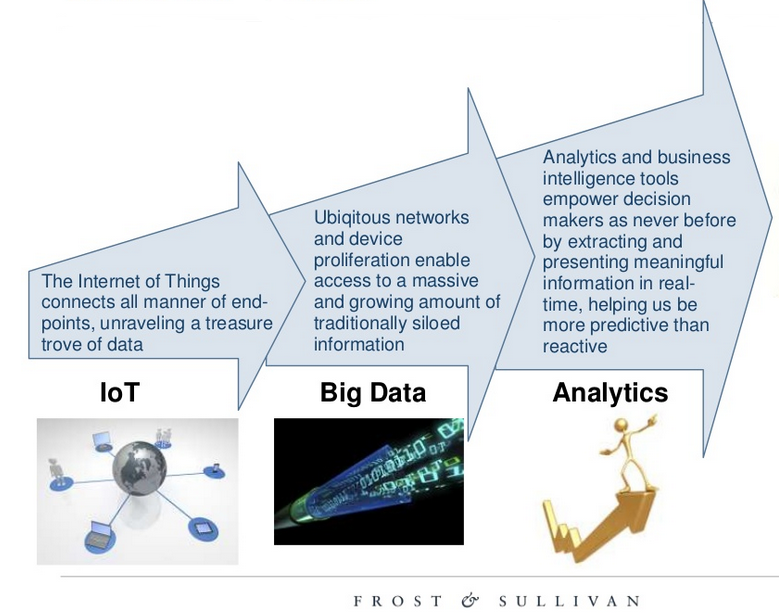
Mukul Krishna, from Frost & Sullivan, presented a simple incremental view of the relationship between the IoT and big data. In short, IoT devices can be thought of as data sources. These data sources generate an incredible amount of data – much of which was previously not accessible. The information and insights from big data allow for better decision-making.

The amount of big data created each day in 2012 was 2.5 exabytes (2.5×1018). In 2014 the amount of data were created each day was 2.3 zettabytes (2.3×1021),
An IDC forecast shows that the Big Data technology and services market will grow at a 27% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) to $32.4 billion through 2017 – or at about six times the growth rate of the overall information and communication technology market.
The need for a plan
McKinsey & Company offer sage advice: put a plan in place.
The payoff from joining the big-data and advanced-analytics management revolution is no longer in doubt. The tally of successful case studies continues to build, reinforcing broader research suggesting that when companies inject data and analytics deep into their operations, they can deliver productivity and profit gains that are 5 to 6 percent higher than those of the competition. The promised land of new data-driven businesses, greater transparency into how operations actually work, better predictions, and faster testing is alluring indeed.
But that doesn’t make it any easier to get from here to there.
So how does one get from here to there?
The answer, simply put, is to develop a plan. Literally. It may sound obvious, but in our experience, the missing step for most companies is spending the time required to create a simple plan for how data, analytics, frontline tools, and people come together to create business value. The power of a plan is that it provides a common language allowing senior executives, technology professionals, data scientists, and managers to discuss where the greatest returns will come from and, more important, to select the two or three places to get started.
What impact has the IoT and big data had on your company? Does your company have a plan in place?

by Fronetics | Dec 17, 2014 | Big Data, Blog, Data/Analytics, Internet of Things

The Internet of Things (IoT) is ubiquitous. Because of this it can seem abstruse. Puneet Mehta does a great job of putting the concept in layman’s terms: “[A] plethora of “dumb” objects becom[ing] connected, sending signals to each other and alerts to our phones, and creating mounds of “little data” on all of us that will make marketers salivate.”
The mounds of data created by the advent of the IoT does not just make marketers salivate. Gartner predicts that the IoT will add $1.9 trillion in value to the economy by 2020. Looking ahead, Cisco estimates that the IoT will create over $14 trillion in value over the next 10 years.
In 2003 there were 500 million connected devices. Cisco estimates that this number will increase to 50 billion by 2020. Morgan Stanley believes this number will be higher – it estimates there will be 75 billion IoT devices by 2020.
“Dumb” objects are becoming connected; the physical and digital worlds are converging. Mounds of data are being collected.
IoT and Big Data
Mukul Krishna, from Frost & Sullivan, presented a simple incremental view of the relationship between the IoT and big data. In short, IoT devices can be thought of as data sources. These data sources generate an incredible amount of data – much of which was previously not accessible. The information and insights from big data allow for better decision-making.

The amount of big data created each day in 2012 was 2.5 exabytes (2.5×1018). In 2014 the amount of data were created each day was 2.3 zettabytes (2.3×1021),
An IDC forecast shows that the Big Data technology and services market will grow at a 27% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) to $32.4 billion through 2017 – or at about six times the growth rate of the overall information and communication technology market.
The need for a plan
McKinsey & Company offer sage advice: put a plan in place.
The payoff from joining the big-data and advanced-analytics management revolution is no longer in doubt. The tally of successful case studies continues to build, reinforcing broader research suggesting that when companies inject data and analytics deep into their operations, they can deliver productivity and profit gains that are 5 to 6 percent higher than those of the competition. The promised land of new data-driven businesses, greater transparency into how operations actually work, better predictions, and faster testing is alluring indeed.
But that doesn’t make it any easier to get from here to there.
So how does one get from here to there?
The answer, simply put, is to develop a plan. Literally. It may sound obvious, but in our experience, the missing step for most companies is spending the time required to create a simple plan for how data, analytics, frontline tools, and people come together to create business value. The power of a plan is that it provides a common language allowing senior executives, technology professionals, data scientists, and managers to discuss where the greatest returns will come from and, more important, to select the two or three places to get started.
What impact has the IoT and big data had on your company? Does your company have a plan in place?

by Fronetics | Oct 2, 2014 | Big Data, Blog, Data/Analytics, Strategy, Supply Chain

Big data is big. It is revolutionary. It is transformative. But what the heck is it?
MIT’s Technology Review does a great job of outlining the hype and the confusion around big data:
“There is unanimous agreement that big data is revolutionizing commerce in the 21st century. When it comes to business, big data offers unprecedented insight, improved decision-making, and untapped sources of profit.
And yet ask a chief technology officer to define big data and he or she will stare at the floor. Chances are, you will get as many definitions as the number of people you ask. And that’s a problem for anyone attempting to buy or sell or use big data services—what exactly is on offer?”
Research conducted by Accenture highlights this dichotomy. Eight-nine percent of survey respondents reported that they believe big data will revolutionize business operations in the same way that the Internet did. Seventy-nine percent of respondents reported that “companies that do not embrace big data will lose their competitive position and may face extinction.” However, the research found that companies hold “differing views of data sources and uses,” and that “valuable data sources are omitted or overlooked.”
Big data and the supply chain
Accenture’s Global Operations Megatrends research looked at big data analytics in the supply chain. Ninety-seven percent of supply chain executive reported that big data analytics can benefit their supply chain. Their expectations for big data analytics include: creating an organizational ability to react more quickly to changes (48 percent); helping their company gain insights about the future (45 percent); and achieving a cross-functional view of the supply chain with the objective of optimizing overall supply chain performance (43 percent).
Although the majority of executives believe big data analytics will benefit their supply chain only 17 percent of survey respondents reported that their company has already implemented analytics in one or more supply chain processes/functions. Accenture makes this supposition:
“While there is considerable hype about, and a high level of general awareness of the value of, ‘big data,’ many companies still do not fully understand how to apply analytics to this data to drive higher supply chain (and overall enterprise) performance.”
Given Accenture’s research, as well as that conducted by Jonathan Stuart Ward and Adam Barker at the University of St Andrews in Scotland, I’d take this one step further. In spite of the hype (or perhaps because of it) there remains confusion regarding what big data actually is. Without a clear definition and understanding of big data, it is (and will continue to be) a challenge to implement big data analytics. Before we realize transformation we need to get to understanding.

by Fronetics | Oct 2, 2014 | Big Data, Blog, Data/Analytics, Strategy, Supply Chain

Big data is big. It is revolutionary. It is transformative. But what the heck is it?
MIT’s Technology Review does a great job of outlining the hype and the confusion around big data:
“There is unanimous agreement that big data is revolutionizing commerce in the 21st century. When it comes to business, big data offers unprecedented insight, improved decision-making, and untapped sources of profit.
And yet ask a chief technology officer to define big data and he or she will stare at the floor. Chances are, you will get as many definitions as the number of people you ask. And that’s a problem for anyone attempting to buy or sell or use big data services—what exactly is on offer?”
Research conducted by Accenture highlights this dichotomy. Eight-nine percent of survey respondents reported that they believe big data will revolutionize business operations in the same way that the Internet did. Seventy-nine percent of respondents reported that “companies that do not embrace big data will lose their competitive position and may face extinction.” However, the research found that companies hold “differing views of data sources and uses,” and that “valuable data sources are omitted or overlooked.”
Big data and the supply chain
Accenture’s Global Operations Megatrends research looked at big data analytics in the supply chain. Ninety-seven percent of supply chain executive reported that big data analytics can benefit their supply chain. Their expectations for big data analytics include: creating an organizational ability to react more quickly to changes (48 percent); helping their company gain insights about the future (45 percent); and achieving a cross-functional view of the supply chain with the objective of optimizing overall supply chain performance (43 percent).
Although the majority of executives believe big data analytics will benefit their supply chain only 17 percent of survey respondents reported that their company has already implemented analytics in one or more supply chain processes/functions. Accenture makes this supposition:
“While there is considerable hype about, and a high level of general awareness of the value of, ‘big data,’ many companies still do not fully understand how to apply analytics to this data to drive higher supply chain (and overall enterprise) performance.”
Given Accenture’s research, as well as that conducted by Jonathan Stuart Ward and Adam Barker at the University of St Andrews in Scotland, I’d take this one step further. In spite of the hype (or perhaps because of it) there remains confusion regarding what big data actually is. Without a clear definition and understanding of big data, it is (and will continue to be) a challenge to implement big data analytics. Before we realize transformation we need to get to understanding.



