Sourcemap: doing well by doing good.
Leonardo Bonanni’s company, Sourcemap, is doing well by doing good, and he’s helping companies to do the same. In working on his doctoral thesis at MIT, Leonardo Bonanni created a service that is good for the world on many levels – it saves companies money and it works towards sustainability through transparency. Bonanni is bringing the people what they want. Consider these numbers from recent surveys:
- more than 88% of consumers think companies should try to achieve their business goals while improving society and the environment
- 83% of employees would seriously consider leaving their job if their employer used child labor in sweatshop factories
- 65% would seriously consider leaving their job if their company harmed the environment
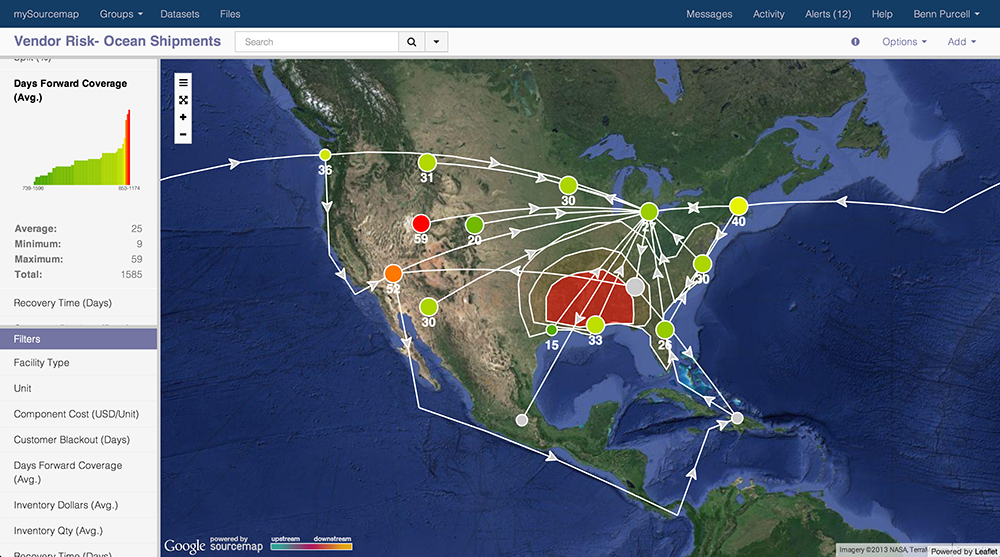
Bonanni’s innovative company, Sourcemap, helps clients visually map the supply chain route, from raw materials to end-users, providing unique and important visibility. Companies like Stoneyfield, Mars Chocolate, Fairphone, and Office Depot can see risks and disruptions in the supply chain in real time, act responsibly, promote sustainability, and please consumers who are increasingly curious and conscientious about materials sourcing.
The likes of the Wall Street Journal, Forbes, and The Guardian have taken interest in Dr. Bonanni and Sourcemap. Here he shares some insights with Fronetics on the growth of the company and how he won’t rest until mapping the supply chain is status quo.
What’s the most exciting thing going on at Sourcemap right now?
2015 is the year of supply chain mapping. When we started helping companies trace their products to the source, it was 2007 and the question was ‘why would we want to do that?’ Today it’s ‘how fast can we start?’ Whether it’s risk, sustainability, or simply finding more efficient ways to source products, companies need a big picture of the end-to-end supply chain. What’s exciting is how fast and far we help our clients get there – sometimes in as little as one day.
Tell me about how the maps are built. Are the maps on the free source platform built the same way as the maps on the enterprise platform?
Sourcemap started as a service for consumers to find out where products come from (free.sourcemap.com is still the only website where anyone can make a supply chain map, no training required). Users log in and map a supply chain – from raw material to end customer – as easily as drawing dots and lines on a Google map. Soon after the free website launched manufacturers approached us to see if we could help them figure out where their products come from. We had a lot of experience from serving millions of visitors through our free website, so we knew how to make a robust and intuitive interface for supply chain mapping. We adapted the technology to enterprise needs by adding company specific KPI’s, network analytics, and real-time reporting. The difference is that our enterprise users don’t draw the supply chains one link at a time. Their maps are automatically generated in near-real time from transportation, purchasing, and product lifecycle management databases.
Is it hard to convince businesses that there is an economic or competitive advantage to a utilizing a platform like Sourcemap?
It’s true that Sourcemap was originally built for sustainability, and it can be hard for companies to dedicate resources to long-term issues when short-term priorities come up every day. But our first success wasn’t helping companies be more sustainable in the long term. It was helping them tackle short-term crises, by developing a supply chain repository for emergency response and business continuity planning. Our clients were spending days and weeks to determine how a natural or human-made disaster was impacting any of thousands of suppliers worldwide. We brought that time down to minutes. Then supply chain managers started to see the benefit of knowing not just who they buy from, but who their suppliers buy from – and making decisions to consolidate or diversify supply, move inventories around, and decide when to in-source / out-source processes. These decisions represent huge savings in overall supply chain cost.
This is fantastic tool for companies who are proud of their supply chains, but what about those companies who aren’t, or who aren’t even fully aware of the steps and impact of their chain?
Over the years we’ve worked with companies big and small, with widely differing visibility into their supply chains. What we’ve seen is that the biggest benefit – the low-hanging fruits – are there for first-time supply chain mappers. These are companies that have expanded through acquisitions, are entering new markets or introducing new products – basically any organization that needs to account for a whole new way of doing business. Then, supply chain mapping is the easiest way to keep tabs on everyone in the supply chain and make sure that decisions are taken with an eye on the big picture.
In the years you’ve been doing this work have you seen a shift in consumer demand around the sourcing of materials and making of products? Is there increasing social pressure for companies to “do good”?
We’ve seen two drivers for supply chain sustainability and transparency: companies who want to attract the best talent, and brands looking to differentiate their product by providing information on its price, its composition, or its source.
Given that you teach at Columbia, I’m wondering if you see a difference in the passion, awareness, and attitude around sustainability with younger generations? Have you seen growth in the enrollment numbers in your classes?
I like to teach one or two evening classes a year (this Fall at NYU) to see how supply chain thinking is evolving as it becomes more mainstream. My class hasn’t changed much since it started in 2007, but the students have. Sustainability used to be a futuristic concern, and no one outside logistics departments ever talked about supply chains. Today there is a real desire among students to be social entrepreneurs, and part of that means thinking about products and services holistically – making sure that the social and environmental impacts are drivers of innovation, not just a nice-to-have. Enrollment has grown, and so has the number of departments where supply chains play a role: from engineering, architecture and design to business, public policy and international affairs.
Has social media played a role in the growth of the business and/or the operations of the business?
Sourcemap wouldn’t be here without social media. The fact that our supply chain maps can be embedded in other websites attracted over a million visitors in the first year. We saw brands embedding maps of their supply chains on their own websites, and we got a tremendous amount of traffic from being embedded and linked from the Huffington Post, Wired and Fast Company.
What are your ultimate goals for Sourcemap?
Supply chain mapping – knowing where products originate – gets easier the more companies do it. It requires information sharing, which means tighter collaboration between buyers and sellers. We’ve seen it become a requirement of purchasing departments: if you want to sell your products, disclose the raw material origins. That makes it easier to trust – and verify – the quality, the compliance, the sustainability of the product. Personally, I won’t rest until supply chain mapping becomes part of doing business as usual.
Dr. Leonardo Bonanni is Founder and CEO of Sourcemap, the supply chain mapping company. The New York-based startup offers enterprise software for companies to trace products, evaluate social, environmental and financial risks, and monitor improvements over time. One day soon you’ll be able to scan a product on a store shelf and be connected to the people who made it through the Sourcemap social network.
Leo is a supply chain transparency advocate named among the 100 Most Influential People in Business Ethics (2011) and America’s Most Promising Social Entrepreneurs (2012). He teaches sustainability at Columbia and at MIT, where he received his doctorate from the MIT Media Lab. He has a background as an architect, an inventor and a performer.
Fronetics Strategic Advisors is a leading management consulting firm. Our firm works with companies to identify and execute strategies for growth and value creation.
Whether it is a wholesale food distributor seeking guidance on how to define and execute corporate strategy; a telematics firm needing high quality content on a consistent basis; a real estate firm looking for a marketing partner; or a supply chain firm in need of interim management, our clients rely on Fronetics to help them navigate through critical junctures, meet their toughest challenges, and take advantage of opportunities. We deliver high-impact results.
We advise and work with companies on their most critical issues and opportunities: strategy, marketing, organization, talent acquisition, performance management, and M&A support.
We have deep expertise and a proven track record in a broad range of industries including: supply chain, real estate, software, and logistics.

