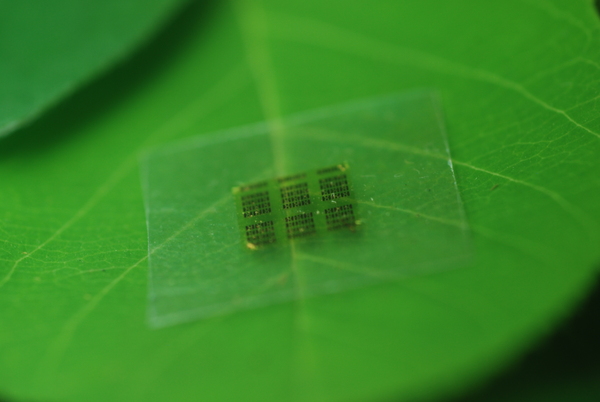
Source: University of Wisconsin -Madison
In 2014 the global consumer electronic market was valued at $1,224.8 billion. Future Market Insights projects that the market will reach $2,976.1 billion by 2020, reflecting a CAGR of 15.4% during the forecast period, 2015 – 2020. As the industry grows, driven by our desire for new technology, so does the amount of electronic waste (e-waste).
Right now 70% to 80% of our old gadgetry goes straight into landfills. According to research firm MarketsandMarkets, the global volume of e-waste generated is expected to reach 93.5 million tons in 2016, up from 41.5 million tons in 2011 at a compound annual growth rate of 17.6%. This waste contains hazardous materials which are harmful to human health and to the environment and are both non-renewable and non-biodegradable.
Semiconductor chips are one of the contributors to the hazardous materials found in e-waste. Researchers at the University of Wisconsin recently announced that they have created a new computer chip – one that is biodegradable and one which reduces the amount of semiconducting material used in manufacturing by a factor of up to 5,000. In spite of these changes, the new chip performs at the same level as traditional chips.
The new computer chip retains the active components of traditional chips, but in the base layer the new chip replaces silicon with cellulose nanofibril (CNF), a flexible, biodegradable material made from wood. This change means that the computer chip can decompose in nature.

The new computer chip wrapped around a tree branch. Source: Nature Communications
In a press release Zhenqiang “Jack” Ma, research lead and UW-Madison electrical and computer engineering professor, says this about the new chips: “Now the chips are so safe you can put them in the forest and fungus will degrade it. They become as safe as fertilizer.”
While these new chips are game-changing with respect to human health and the environment, they are also poised to transform the consumer electronics industry. The transformative nature of the chips, and the one that will likely be the tipping point to adoption, is their transparency and flexibility.
Ma’s new chips are ready for commercialization.