
by Fronetics | Oct 19, 2017 | Blog, Leadership, Strategy, Talent
Investing in your employees through wages, time and energy can have a big impact on your company’s productivity.
Successful companies understand that employees’ job satisfaction and engagement affect productivity. After all, employees are an extension of your business. Keeping them challenged and encouraged is key to their success, as well as the overall success of your company. In research for their book, Time, Talent, and Energy, Bain partners Michael Mankins and Eric Garton discovered that investing in your employees does, in fact, pay off for companies. “The top-quartile companies in our study unlocked 40% more productive power in their workforce through better practices in time, talent and energy management,” says Garton.
Here are the 3 investments that Mankins and Garton found most impactful to productivity.
3 investments that will invigorate productivity
1) Wages
Three economists studied OECD data representative of the whole population of businesses in 16 countries around the world. They found that firms paying higher wages were reporting higher productivity. The link between the two seems pretty basic: Pay workers higher wages and they will feel valued and be more productive at their jobs.
But many companies believe that higher wages come at the cost of their consumers. This doesn’t have to be the case. Dan Teran, chief executive of Managed by Q, is a thought leader in higher wages creating a culture of respect and productivity.
“Teran believes that most American businesses, and especially fast-growing start-ups like Uber, have mistaken short-term gains for long-term value, undercutting the share of revenue that flows to workers in a way that will perversely hurt their bottom line. He believes, even more radically, that decades of rising inequality and stagnant wages in America are not an inevitable byproduct of capitalism; instead, they come from a simple misunderstanding about how best to deploy workers and recognize the value they bring to a company.” Managed by Q’s ‘Good Job’ Gamble, Adam Davidson
From small businesses like Managed by Q to retail giants like Walmart, the ideology behind better wages and benefits is catching on. Companies are understanding the relationship between production and pay and trying to narrow the gap.
2) Time
The pressure of working long hours and being available around the clock has a lasting effect on employees. Such practices often lead to burnt out, overworked team members. In fact new research suggests that, on average, managers have fewer than 7 hours per week of uninterrupted time to do deep work. Their days are filled with meetings, responding to emails, and having short increments of time to complete tasks.
The average company loses more than 25% of its productive power to organizational drag, processes that waste time and prevent people from getting things done. Meetings that last too long and processes that move too slowly contribute to lower productivity, less quality work, and low employee morale.
Allowing employees the time to feel creative and focused on their projects will lead to breakthroughs in productivity. Try establishing quiet hours for certain times of the day to encourage workers to spend more uninterrupted time deep thinking, which can lead to innovative and fresh ideas.
3) Energy
An inspired employee is more than twice as productive as a satisfied employee and more than three times as productive as a dissatisfied employee. Yet, only one in eight employees are inspired. One of the most beneficial things a company can do is to inspire its employees. Engaged working environments and positions that allow creative and innovative thought will lead to increased employee engagement and productivity.
Companies like Apple, Netflix, Google and Dell are 40% more productive than the average company. Why is that, you ask? These companies invest in inspiring their employees.
“Inspirational leadership can be taught. Companies that recognize that and invest in making it happen create meaningful impact on the productivity of their company,” says Mankins. Studies have shown that employees that feel satisfied with their jobs are more productive.
Give your employees the autonomy to feel engaged in their work. This freedom will give them the opportunity to get creative and involved in their projects.
The opportunity exists for all employers to positively affect worker happiness while simultaneously increasing productivity. If your company is interested in exploring the benefits of investing in their employees, focusing on wages, time and energy is a good place to start. You might be surprised to find currently untapped financial gains just by putting investment in your employees at the top of your priority list.
Related posts:


by Fronetics | Oct 22, 2015 | Blog, Leadership, Strategy, Talent

Do we need to rethink the concept of happiness at work?
Do you like your job? It can be a complex question to answer when everything is taken into account. For some people that question is comprised of several other questions, many of which have different answers: If I could do anything with my life would I be working this job? Is this job my passion? Would I work as many hours if I didn’t have to? Do I feel productive? Is my work/life balance ok? Am I happy?
On average, Americans put in about 1,700 hours a year, which is much more than the French and Germans, but much less than the Koreans or Singaporeans. For Americans, this breaks down to 34.4 hours a week considering vacation time and holidays, however many adult, full-time employees report working more than 34 hours week. According to a Gallup poll, 4 in 10 workers reported putting in 50+ hours per week. So are all these hours bringing us happiness? First, let’s have a look at what happiness is.
People have always had a lot to say about happiness. Artistotle said, “Happiness depends upon ourselves.” Albert Camus said, “You will never be happy if you continue to search for what happiness consists of. You will never live if you are looking for the meaning of life.” The Dali Lama says, “Happiness is not something ready made. It comes from your own actions.” What is certain is that we seem to have a happiness obsession. We want it, we seek it, we’re told we need it so we believe we need it.
Harvard psychologist, Dan Gilbert, believes that happiness is not always entirely in our control and not entirely out of our control, and sometimes we feel it and sometimes we don’t. That’s ok, he says. In a TED Talk on happiness he says, “Happiness doesn’t last that long. Happiness is an emotion — it’s a feeling. The human brain isn’t built to sustain a feeling over the long term…Your emotions are a compass. They’re telling you which direction to go in. When you feel bad you turn left, you try something different in your life. When you feel good you keep on marching in the direction you’re going. What good would a compass be if it were perpetually stuck on north?”
So if we can’t feel happy all the time, and we don’t need to feel happy all the time, then why are we told we should feel happy all the time? Workplaces have been increasingly focused on employee happiness. Several studies have shown that happy employees are more productive and more loyal. Even tycoon Richard Branson is on board with this idea, “Your employees are your company’s real competitive advantage. They’re the ones making the magic happen—so long as their needs are being met.” How can the Virgin god be wrong?
A new article in the Harvard Business Review has gathered many studies and theories opposing the contemporary idea that happiness in the workplace is the key to success. The authors point to studies that show that people fail to feel happy when they are expected to be happy, that people can become emotionally vulnerable and needy when they expect their workplace to fulfill their happiness, that people may be more selfish when happy, and that people who value happiness often feel lonelier. The studies also pointed out that angry employees were better at negotiating than happy employees and better at intuiting actions of deception.
Perhaps our thinking about happiness needs to shift. Perhaps we don’t need employees bounding around the office with endless smiles. Perhaps the expectation we have for employees to be happy, and employers to be responsible for that happiness, is all too much. According to Dr. Vanessa Boute, a social psychologist, “One of the misconceptions about happiness is that happiness is being cheerful, joyous, and content all the time; always having a smile on your face. It’s not – being happy and leading rich lives is about taking the good with the bad, and learning how to reframe the bad.”
Fronetics Strategic Advisors is a leading management consulting firm. Our firm works with companies to identify and execute strategies for growth and value creation.
We advise and work with companies on their most critical issues and opportunities: strategy, marketing, organization, talent acquisition, performance management, and M&A support.
by Fronetics | Jul 3, 2015 | Blog, Leadership, Strategy, Talent

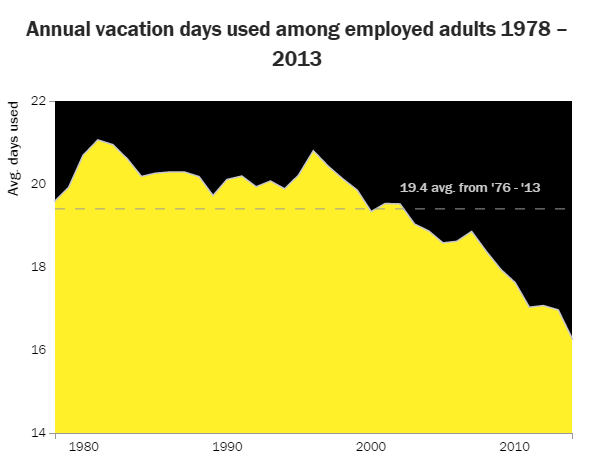
In 1983, the year that Chevy Chase loaded his movie family into the Griswold’s station wagon in National Lampoon’s Vacation, Americans took an average of 20 vacation days. Now, the youngest member of the Griswold family is back on the big screen in 2015, this time taking his own family on a vacation. If Americans’ recent use of paid time off is any indication, reports suggest he’ll see a more open road than his father. Plummeting to an average of 16 vacation days in 2013, the time that Americans spend away from work has fallen precipitously over the past decade. And neither workers nor employers are benefiting from this marked decline.

Source: Project Time Off, Oxford Economics, 2014
You Need a Vacation
Occasionally escaping daily routine is central to both the physical and mental health of employees, and taking time off has been proven to boost work performance and productivity. A 2011 Harvard Medical School study found that sleep deprivation costs American companies $63.2 billion a year in lost productivity. Ernst & Young conducted an internal study of its employees in 2006 and found that for each additional 10 hours of vacation employees took, their year-end performance ratings from supervisors (on a scale of one to five) improved by 8%. What’s more, retention rates were significantly higher among vacationers.
Wish You Were(n’t) Here
Given that the Center for Economic Policy and Research reports that the United States is the only advanced economy in the world that does not guarantee its employees paid time off, it’s unlikely the use of vacation days will increase without some type of policy reform. With American employers not legally required to give workers either paid vacation time or paid holidays, a high number – 77% of private sector companies offer paid time off and paid holidays as part of employee compensation packages. Not surprisingly, though, as employee wage increases, so does the likelihood that they will receive time off; half of low-wage workers typically receive paid time off whereas more than 90% of high-wage workers receive paid time off.
Unplug and Unwind
Harris Interactive reports that people like the idea of more time off. Specifically, 50% of workers who receive paid vacation time in the top 10 cities in the US say they would be willing to sacrifice a workplace benefit for more paid time off. Ironically, although employees say they want more time off, 57% don’t take off the time they already receive. Each year there are 175 million vacation days which American workers are entitled to which are not taken. Even when employees actually do use their time off, they don’t spend the time unplugged. 47% of respondents in a recent survey by Pertino reported that they feel less stressed on vacation if they can stay connected to the office. The same study found that 59% of Americans regularly work, check email, take a phone call, and do other work related tasks while on vacation. But, aside from increased productivity upon their return, employers have another incentive to encourage employees to unplug while away. The Pertino survey found that 77% of those who work on their vacation do not have access to their office network. Because of this, employees use unsanctioned or unsecured cloud services (32%) and/or bring their work computers and files with them on vacation (35%). Public Wi-Fi hotspots are commonly used by vacationers, creating an opportunity for company data and/or log-in credentials to be stolen.
While there are certainly many factors at play in the 2013 job satisfaction study published by the non-profit research group Conference Board, it’s worth noting that back in 1987, when the average American worker took 20 days of vacation, job satisfaction stood at over 61%. Now that Americans have cut back on days away from the office, job satisfaction hovers slightly above 50%. There’s no definite way to tell if Americans could move the needle of job satisfaction by loading up their cars and hitting the open road, but it’s a good start. Let’s start making vacations work for us.
Fronetics Strategic Advisors is a leading management consulting firm. Our firm works with companies to identify and execute strategies for growth and value creation.
Whether it is a wholesale food distributor seeking guidance on how to define and execute corporate strategy; a telematics firm needing high quality content on a consistent basis; a real estate firm looking for a marketing partner; or a supply chain firm in need of interim management, our clients rely on Fronetics to help them navigate through critical junctures, meet their toughest challenges, and take advantage of opportunities. We deliver high-impact results.
We advise and work with companies on their most critical issues and opportunities: strategy, marketing, organization, talent acquisition, performance management, and M&A support.
We have deep expertise and a proven track record in a broad range of industries including: supply chain, real estate, software, and logistics.


by Fronetics | Apr 15, 2015 | Blog, Leadership, Strategy, Talent

You might be surprised to find currently untapped financial gains just by putting employee happiness at the top of your priority list.
The way we work has fundamentally changed. There’s no doubt it is still evolving, but what we know about the way we work is that it can no longer be summed up by the decades-old “going to work” experience. Company-owned buildings, offices, and cubicles are no longer required to accommodate employees and the growing trend of companies offering flexible scheduling and remote work options for employees has substantial implications. There’s good news in that these new employment structures are impacting employee satisfaction and productivity in ways that employees and employers alike can celebrate.
Of the most significant factors affecting employee satisfaction is the employee-manager relationship. Communication is essential for relationships to flourish – especially employee-manager relationships. A recent Gallup poll found that employee engagement was highest among those with daily communication with their managers. By leveraging digital communication tools, employees who work remotely are able to have just as much, if not more, interaction with supervisors. Consistent, regular access to management creates a culture of connectedness and accountability – a culture where employee satisfaction is high. Not only does this allow for nimble adaptations in project approach or client strategy, but the immediate feedback loop positively affects employee engagement and motivation. The emergence of this unique employee-manager structure has allowed for managers to effectively monitor work and provide meaningful feedback, but to avoid micromanagement.
The most effective managers have been shown to be the ones who have respect for their employees as individuals. These managers actively work to help their employees find an ideal work-life balance. Recognizing and responding accordingly to situations where employees are disengaged, either physically or emotionally, from their work responsibilities is at the heart of building a relationship of trust and conviction.
Even though remote work arrangements seem to run counterintuitive to expanding the capacity of workplace productivity, giving employees the flexibility to fit work around their life actually improves worker productivity. The effects of building a company culture where employee satisfaction is valued translates into increased efficiency. That is, a happy and well-managed staff is likely to stay engaged, motivated, and committed to company objectives.
The flexibility that working remotely provides makes it easier for workers to strike their ideal work-life balance. A significant finding emerged from a 2000 study in which researchers found that on average workers reached peak productivity in their 30s and 40s. Most often concurrently, these same workers are tasked in their home lives with parenting responsibilities and the care of aging parents. Giving employees options to maintain flexible work schedules allows employees to give equal attention to both home and work life, enabling maximum productivity. What’s more, by eliminating commute time and spending less time in meetings, people who work from home actually spend more time working. Some find managing work responsibilities from a quieter environment, as opposed to a noisy office, more conducive to productivity.
Presented with all the benefits flexible scheduling and remote work options have to offer, some companies might find it tempting to quickly implement a flexible work program in order to start realizing benefits. But consider that this new work structuring also brings with it a new set of issues for managers to navigate. Supervising employees who aren’t location-specific and monitoring performance without personally interfacing require companies to put thoughtful initial focus on building a solid communication structure and setting manageable expectations for employees. Clear articulation of these expectations and structures is required for success.
While this type of work structuring might not be a good match for every employee or every workplace, the opportunity exists for employers to positively affect worker happiness while simultaneously increasing productivity. If your company is interested in exploring the benefits of offering flexible scheduling and remote workplaces, consider a trial period or experimental program. You might be surprised to find currently untapped financial gains just by putting employee happiness at the top of your priority list.

by Fronetics | Apr 15, 2015 | Blog, Leadership, Strategy, Talent

You might be surprised to find currently untapped financial gains just by putting employee happiness at the top of your priority list.
The way we work has fundamentally changed. There’s no doubt it is still evolving, but what we know about the way we work is that it can no longer be summed up by the decades-old “going to work” experience. Company-owned buildings, offices, and cubicles are no longer required to accommodate employees and the growing trend of companies offering flexible scheduling and remote work options for employees has substantial implications. There’s good news in that these new employment structures are impacting employee satisfaction and productivity in ways that employees and employers alike can celebrate.
Of the most significant factors affecting employee satisfaction is the employee-manager relationship. Communication is essential for relationships to flourish – especially employee-manager relationships. A recent Gallup poll found that employee engagement was highest among those with daily communication with their managers. By leveraging digital communication tools, employees who work remotely are able to have just as much, if not more, interaction with supervisors. Consistent, regular access to management creates a culture of connectedness and accountability – a culture where employee satisfaction is high. Not only does this allow for nimble adaptations in project approach or client strategy, but the immediate feedback loop positively affects employee engagement and motivation. The emergence of this unique employee-manager structure has allowed for managers to effectively monitor work and provide meaningful feedback, but to avoid micromanagement.
The most effective managers have been shown to be the ones who have respect for their employees as individuals. These managers actively work to help their employees find an ideal work-life balance. Recognizing and responding accordingly to situations where employees are disengaged, either physically or emotionally, from their work responsibilities is at the heart of building a relationship of trust and conviction.
Even though remote work arrangements seem to run counterintuitive to expanding the capacity of workplace productivity, giving employees the flexibility to fit work around their life actually improves worker productivity. The effects of building a company culture where employee satisfaction is valued translates into increased efficiency. That is, a happy and well-managed staff is likely to stay engaged, motivated, and committed to company objectives.
The flexibility that working remotely provides makes it easier for workers to strike their ideal work-life balance. A significant finding emerged from a 2000 study in which researchers found that on average workers reached peak productivity in their 30s and 40s. Most often concurrently, these same workers are tasked in their home lives with parenting responsibilities and the care of aging parents. Giving employees options to maintain flexible work schedules allows employees to give equal attention to both home and work life, enabling maximum productivity. What’s more, by eliminating commute time and spending less time in meetings, people who work from home actually spend more time working. Some find managing work responsibilities from a quieter environment, as opposed to a noisy office, more conducive to productivity.
Presented with all the benefits flexible scheduling and remote work options have to offer, some companies might find it tempting to quickly implement a flexible work program in order to start realizing benefits. But consider that this new work structuring also brings with it a new set of issues for managers to navigate. Supervising employees who aren’t location-specific and monitoring performance without personally interfacing require companies to put thoughtful initial focus on building a solid communication structure and setting manageable expectations for employees. Clear articulation of these expectations and structures is required for success.
While this type of work structuring might not be a good match for every employee or every workplace, the opportunity exists for employers to positively affect worker happiness while simultaneously increasing productivity. If your company is interested in exploring the benefits of offering flexible scheduling and remote workplaces, consider a trial period or experimental program. You might be surprised to find currently untapped financial gains just by putting employee happiness at the top of your priority list.








