
by Fronetics | Feb 5, 2018 | Blog, Content Marketing, Marketing
Internet users are changing how they search, and search engines are changing in response — which means writing for SEO is changing, too. Here’s what you need to know.
I’ve just completed a really detailed, often-complicated series about writing for SEO in today’s changing search landscape. I hope you read all four posts and now have a better understanding of the new way we marketers are thinking about content marketing.
But, as my colleagues occasionally have to remind me, not everyone enjoys the nitty gritty of SEO writing like I do. It’s also important to step back and take a look at the forest after examining the trees.
So here are some really important takeaways from the series — about how internet users, search engines, and writing for SEO are changing — that I think are important for all marketers in the supply chain and logistics industries.
4 things to know in a changing search landscape
1) Search engines are changing.
While keyword rankings used to be the gold standard for measuring SEO success, this is no longer the case. New search algorithms have moved beyond giving everyone the same results of a query, meaning that keyword ranking can change drastically depending on context (like location).
In addition, Google is increasingly showing featured snippets at the top of search results.
What you need to do:
Know that measuring SEO success is no longer as simple as keeping track of keyword rankings. It’s still information worth having, but it’s part of a larger set of metrics you need to evaluate your success and tailor your efforts.
To effectively take advantage of featured snippets, it’s important to structure your content so it’s optimized to appear in this prime location.
Read the full post.
2) People are changing how they search.
Because of the rise of mobile and voice search, people are now searching with a phrase or question rather than a single term. In response, search engine development has focused on natural language processing — meaning search engines now analyze phrases as a whole rather than a keyword. That essentially means they evaluate a site’s content regarding an entire topic rather than its use of a particular word in order to deliver the best answers to users’ queries. Basically, we’re looking at the same issue as the last post, but from the user end.
What you need to do:
Stop trying to rank for a small set of keywords. What’s important is broad visibility across a topic. You should start thinking about the major themes of your content and then build posts and website pages to support them.
Read the full post.
3) Structure your content in topic clusters and pillar content.
Pillar content is your evergreen content that offer a high-level overview of the several ideas/phrases/value propositions that most closely align with your brand. Topic clusters are the subtopics that provide more detail on those high-level ideas of your pillar content. Adding hyperlinks to pillar content pages from topic cluster pages and vice versa creates a structure that signals to search engines that your site has lots of good, well-organized information about a certain topic, which improves ranking across that topic.
What you need to do:
Structure your content into pillar content and topic clusters. Add hyperlinks between the pages. Optimize topic cluster pages to drive traffic and pillar content pages to convert leads.
Read the full post.
4) Measure the success of your content.
Measuring success is getting more complex. You can no longer effectively gauge the effectiveness of campaigns on a post-by-post basis. Instead, measure your visibility across each topic.
What you need to do:
Start looking at the bigger picture. Consider how all content under each cluster topic performs as a whole. As you do this, keep the big four questions in mind:
1) Which topics perform best at driving traffic to your website or other web presence?
2) Which topics earn you the most leads?
3) Which topics drive the most revenue to your business?
4) Which topics earn the most backlinks/coverage?
Read the full post.
Related posts:


by Fronetics | Jan 16, 2018 | Blog, Content Marketing, Marketing
Using topic clusters and pillar content instead of trying to rank for a short list of keywords will boost your search engine rankings and improve user experience.
This week, in our ongoing Writing for SEO series, we’re looking at topic clusters and pillar content. Our previous two posts explored how search engines are changing, and how people are changing the ways they search.
I’ve been hinting — more like, emphasizing — in our recent Writing for SEO series that trying to rank for certain keywords in each blog post you publish is a practice on the way out. You may have been wondering what you’re supposed to do instead. Today’s post on topic clusters and pillar content is your answer.
Before we dive too far in, it’s important to understand the key terms at work here.
- Core topics are the several ideas/phrases/value propositions that most closely align with your brand. These are the categories that define your business and the knowledge you have to share with internet users. You want users searching the for these phrases to find your business. For Fronetics, content marketing and social media marketing for the supply chain are two obvious examples.
- Pillar content is your evergreen content that covers those topics at a high level. For Fronetics, an example would be: Why Supply Chain and Logistics Businesses Need Content Marketing. Pages with pillar content are typically longer, offering a broad overview of the subject and linking to other webpages (cluster pages) that offer more in-depth information about related subtopics.
- Topic clusters are the subtopics that cover a particular aspect of a core topic. For example, writing for SEO, blogging, and content strategy are a topic cluster that falls under the core topic of content marketing.
- Cluster pages are webpages that contain content covering topics from your cluster. Each topic cluster page focuses on providing more detail for a specific keyword relating to the core topic. For example, Instagram Stories: How the Supply Chain Can Use Them to Engage Prospects and Customers (core topic: social media marketing) was one of our most popular topic cluster pages last year.
How to structure your pages
Your pillar content page should contain links to each related topic cluster page, and each cluster page should link back to the pillar content, with the same hyperlinked keyword. This allows visitors to move seamlessly between the pages to find information that is most relevant to them. It also helps search engines better understand the content of your website so it can drive appropriate traffic to your content.
Topic cluster pages should focus on driving traffic from specific queries (e.g., “How do I use Instagram Stories?”). Pillar content pages should include broad information about the core topics, as well as opportunities for website visitors to convert to leads. This sets up your website so that traffic comes in through your cluster pages and converts on your pillar content pages.
As HubSpot puts it, “The beauty of this model is that you can spend a lot more time optimizing your pillar content for conversions and your cluster content for traffic. This saves a lot of time compared to the traditional model of optimizing each individual post.”
Why topic clusters and pillar content
Using topic clusters and pillar content lets you organize your internal linking more efficiently, boost your search ranking, and provide a better user experience.
Because search engines are getting better at understanding semantically related concepts, this structure allows them to recognize your authority on a certain topic — rather than assigning you a ranking based on an exact word or phrase. It shows you have real depth and breadth on a topic, which is important to users searching for information about it.
As I say all the time, search engines are constantly evolving to bring the most relevant content to people who are searching. So if you can show search engines that you have breadth and depth on a topic, they will assign more authority and higher search placement to your website pages.
What’s more, one high performing cluster page can elevate search rankings for all the other pages linked to the same pillar. That means more users will find your content. That means more effective content marketing for you.
So, rather than writing around a short list of keywords for which you’d like to rank, you should focus on developing topic clusters and pillar content that align with your brand to drive organic traffic.
Want to learn more about writing for SEO? Make sure to read the other parts of our series: part 1, Writing for SEO: Search Engines are Changing, part 2, Writing for SEO: People Are Changing How They Search, and part 4, Writing for SEO: Measuring the Success of Your Content.
Related posts:

SaveSave

by Fronetics | Jan 10, 2018 | Blog, Content Marketing, Marketing
Those writing for SEO need to be conscious of how users are being more conversational in their search queries and how search engines are analyzing phrases over keywords.
This is part two of a four-part series about writing for SEO for supply chain marketers.
Last week, we kicked off our Writing for SEO series by taking a look at how search engines are changing. As we delve further into updated strategies for effective SEO writing for supply chain marketers, today we’ll explore the ways in which people are changing their search behaviors, and what that means for your content.
Search queries are turning conversational
Before we start quoting studies and scholarly research, think for a minute about how you search the web, and how that’s changed over the past several years. Chances are, you do lots of searching on your phone, sometimes using voice search. (“Siri, what’s the fastest pizza delivery in my neighborhood?”) And you’re probably “talking” to the internet more like a friend than an encyclopedia.
The studies back us up. According to HubSpot’s blog, “Amplified by the rise of mobile and voice search, queries have become more and more conversational.” A few years ago people tended to enter a single term into a search engine. Now they’re increasingly asking questions and using full, complex sentences.
Search engines are responding. In order to understand this new type of query better, much of Google’s product development in the past 3-4 years has been about natural language processing. The 2013 introduction of Hummingbird, Google’s search algorithm, is a prime example.
Writing for SEO with topics over keywords
Search algorithms like Hummingbird have begun analyzing phrases rather than relying solely on keywords. This is big news for writing for SEO. As Google and other search engines move from keyword to topic-focused SEO, you need to be adjusting your content strategy to maximize your visibility.
We pointed out last week that keyword rankings aren’t as reliable as they used to be. In summary, search engines have evolved beyond the point that everyone gets the same results from a query (depending on location, search history, etc.). Therefore rank can change drastically depending on context. Now we’re looking at the same issue from the user end.
“The traditional view of ‘keywords’ in search has changed,” according to HubSpot. Traditional writing for SEO technique tells us that there were about 10-20 “big keywords” that were sought after for ranking within a topic. Now, there are hundreds or thousands of “long-tale variations” that people regularly search for within a topic — and change based on location.
To boil it all down, it’s no longer enough to dominate a few words. What’s important is broad visibility across a topic.
Make sure to read the other posts in our series, part 1: Writing for SEO: Search Engines are Changing, part 3: Writing for SEO: Topic Clusters and Pillar Content (NOT Keywords), and part 4: Writing for SEO: Measuring the Success of Your Content.
Related posts:

SaveSave
by Fronetics | Jan 3, 2018 | Blog, Content Marketing, Marketing
In part one of a four-part series on writing for SEO, we address how search engines and the search landscape have changed recently.
Content marketing has seen a lot of changes in the past few years. These changes are largely results of the rapidly evolving search landscape, as well as a seismic shift in the way people are actually discovering content. New, more sophisticated search algorithms, changes in the way people use search engines, and new ways that marketers develop their content are just a few of the contributing factors and outcomes.
Over the next few weeks, we’ll be writing a series of posts examining how marketers should approach writing for SEO in this new landscape. Today, we’re exploring specifically how search engines have evolved — something they are always doing, as they improve to help searchers find the content that best answers their queries.
Are keyword rankings still important?
It’s important to recognize that as search engines change the way they process and evaluate content, older metrics of SEO success aren’t as reliable as they used to be. Take keyword rankings for example. While conventional wisdom tells us that it’s absolutely necessary for content marketers to check their Google keyword rankings for target keywords, debate has swirled recently about the actual reliability of this metric.
Why is this once-standard metric being called into question? The answer is largely about context: Search engines have evolved beyond the point where everyone gets the same results of a query, and therefore rank can change drastically depending on context.
Location-based searches are one of the most obvious and important contextual variables. Simply put, depending on where you’re searching from, you’ll see different search results. This makes it difficult and unreliable to evaluate success based on keyword rankings alone.
Featured snippets
In addition to keyword-ranking problems, search engines are starting to dictate how content should be structured — particularly with the increased appearance of featured snippets. These snippets typically display content from within one of the pages ranking on page one of a question-based query, directly answering the question searched for without the user ever having to visit the actual page.
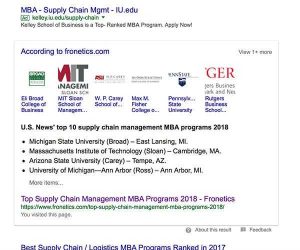
Fronetics has the featured snippet for Supply Chain Management MBA Programs.
A recent study found that of 1.4 million queries, 30% showed a featured snippet — that’s big growth. This means that content that ranks within the featured snippet section often gets a much greater share of the traffic for the given query. For content creators, this points to a need to restructure content to try to appear within these featured snippets.
Changes to the way search engines work do present a challenge for content creators writing for SEO. But keeping pace with the ever-changing technology is key to keeping your content relevant.
Make sure to check out part 2 in our series, Writing for SEO: People Are Changing How They Search, part 3, Writing for SEO: Topic Clusters and Pillar Content (NOT Keywords), and part 4, Writing for SEO: Measuring the Success of Your Content.
Related posts:

SaveSave
by Elizabeth Hines | Oct 8, 2024
Get a free website audit From the supply chain website specialists. The form will redirect to a survey that will collect the information we need to create the audit. How effective is your website? Is your business making the most of its web presence? Discover untapped...







