
by Fronetics | Jul 21, 2015 | Blog, Leadership, Strategy, Supply Chain

A “revolution” is what Pope Francis recently called it – the necessity for humans to change attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors in order create a sustainable ecosystem and society. In his encyclical, entitled Praise be to you – On Care For Our Common Home, he called upon all people and organizations to push against the increasing drive for power at the expense of the earth and other human beings, stating, “We are not faced with two separate crises, one environmental and the other social, but rather one complex crisis which is both social and environmental.”
Pope Francis is one large voice in a sea of voices— secular and non-secular— who have been pleading for change for decades. Recent record-breaking temperatures, storms, and droughts cannot be ignored. What is the role of each person in these battles? What is the role of governments, NGOs, companies?
The supply chain impacts: water, environment, raw materials, energy, animals, humans – essentially the entire planet and those who exist on it.
Cathy Morris, senior vice president and chief strategy officer for Arrow Electronics, Inc., calls attention to the fact that “everything hinges on an effective supply chain.” Specifically: “Products can be made, money can be invested, ideas can be brought to fruition, but without the supply chain everything stops.” The scope of influence of this trillion dollar industry has a significant impact on our planet and our environment.
In an interview with the Harvard Business Review, Peter Senge states that the perception of sustainability must shift, “They might not say this, but most companies act as if sustainability is about being less bad. There’s certainly a need to reduce your carbon footprint. But people don’t get excited about incremental changes like that. They need a more ambitious vision.”
The supply chain holds within it the power to impact many things, from stocking your grocery and clothing stores, to making the cars you use to get to those stores, or the pieces of the computer you use to purchase those things online. The supply chain is also the packing and the raw materials to make the packing. It’s the boat, the truck, the train, and the plane to move the materials. From the products to the moving of products, there are few areas of daily living that does not involve the supply chain.
The supply chain also holds within it the power to impact the sustainability of the ecosystem. In the past several decades we have seen increasing evidence that human behavior is altering the state of the earth. According to PWC, “While climate change and increasing temperatures now seem inevitable, there are high levels of uncertainty about the manifestations and magnitude of their impact. What is certain, though, is that climate change will have a multiplier effect on supply chain risk.”
In the 1980s we saw that we, as individuals, were contributing to the hole in ozone layer by emitting man-made gases. Although the ozone appears to be slowly recovering, a larger issue looms: greenhouse gases. The three main gases that traps and heat the earth, Carbon Dioxide (72% of total), Methane (18% of total), and Nitrous Oxide (9% of total), come from our need for energy (power stations 21.3% and Fossil fuel retrieval 11.3%), products (industrial processes (16.8%), transportation (14%), and food (agricultural byproducts) 12.5%) rounding out the top emitters by sector.
In our contemporary pursuit for an easier life, people consume more products, energy, and water. We desire heat when it’s cold, air-conditioning when it’s hot. We want to travel in cars and planes. We want more, better, faster, cheaper. According to the NASA website, “In its Fourth Assessment Report, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, a group of 1,300 independent scientific experts from countries all over the world under the auspices of the United Nations, concluded there’s a more than 90 percent probability that human activities over the past 250 years have warmed our planet.” The same report showed that “climate change is a material risk to supply chains across industries, and according to the CDP, more than 50 percent of an average corporation’s carbon emissions typically come from the supply chain.”
According to BSR’s report, Business Action for Climate-Resistant Supply Chains, there are five areas of supply chain climate risks that require consideration by all companies:
- The physical risk to suppliers’ assets and operations
- The risk of reduced availability or increased costs of inputs
- The risk of changing regulations in sourcing or distribution markets
- The risk of climate-related disruptions in communities that impact supplier workforce availability and productivity
- Stakeholder, or reputational, risk
We know the facts, we know much of the damage, so now what? Humans contribute, the supply chain contributes. At this point people want to move beyond the blame game and work to improve and, in some cases, reverse the damage. There’s an expectation that individuals will help in this effort, driving more efficient cars, finding renewable sources of energy, and focusing on recycling, but companies are also being asked to do their part, particularly the vast world of the supply chain. According to the UN Global Compact website, “A company’s entire supply chain can make a significant impact in promoting human rights, fair labour practices, environmental progress and anti-corruption policies. However, UN Global Compact participants rank supply chain practices as the biggest challenge to improving their sustainability performance.”
Fronetics Strategic Advisors is a leading management consulting firm. Our firm works with companies to identify and execute strategies for growth and value creation.
Whether it is a wholesale food distributor seeking guidance on how to define and execute corporate strategy; a telematics firm needing high quality content on a consistent basis; a real estate firm looking for a marketing partner; or a supply chain firm in need of interim management, our clients rely on Fronetics to help them navigate through critical junctures, meet their toughest challenges, and take advantage of opportunities. We deliver high-impact results.
We advise and work with companies on their most critical issues and opportunities: strategy, marketing, organization, talent acquisition, performance management, and M&A support.
We have deep expertise and a proven track record in a broad range of industries including: supply chain, real estate, software, and logistics.

by Fronetics | Jul 20, 2015 | Blog, Logistics, Marketing, Social Media, Strategy, Supply Chain

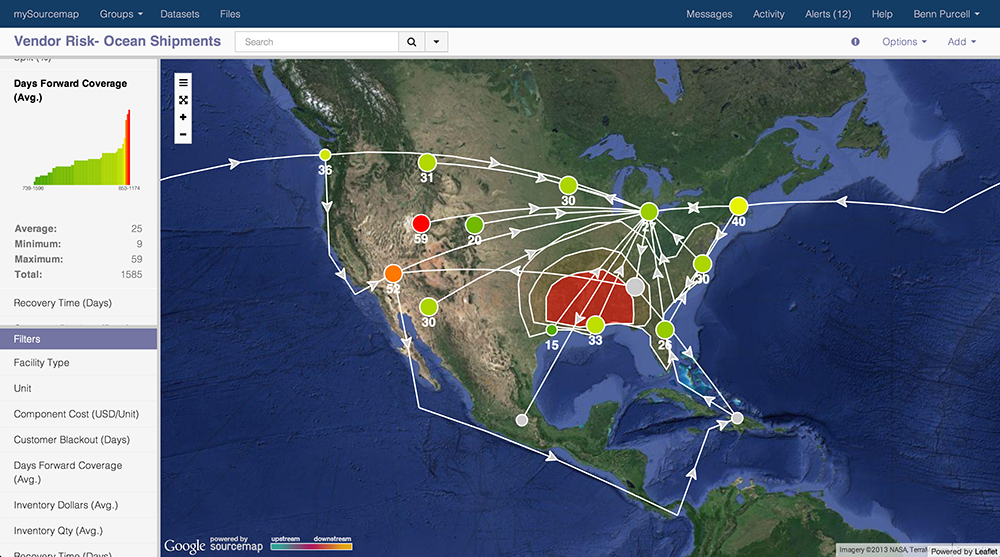
Sourcemap: doing well by doing good.
Leonardo Bonanni’s company, Sourcemap, is doing well by doing good, and he’s helping companies to do the same. In working on his doctoral thesis at MIT, Leonardo Bonanni created a service that is good for the world on many levels – it saves companies money and it works towards sustainability through transparency. Bonanni is bringing the people what they want. Consider these numbers from recent surveys:
- more than 88% of consumers think companies should try to achieve their business goals while improving society and the environment
- 83% of employees would seriously consider leaving their job if their employer used child labor in sweatshop factories
- 65% would seriously consider leaving their job if their company harmed the environment
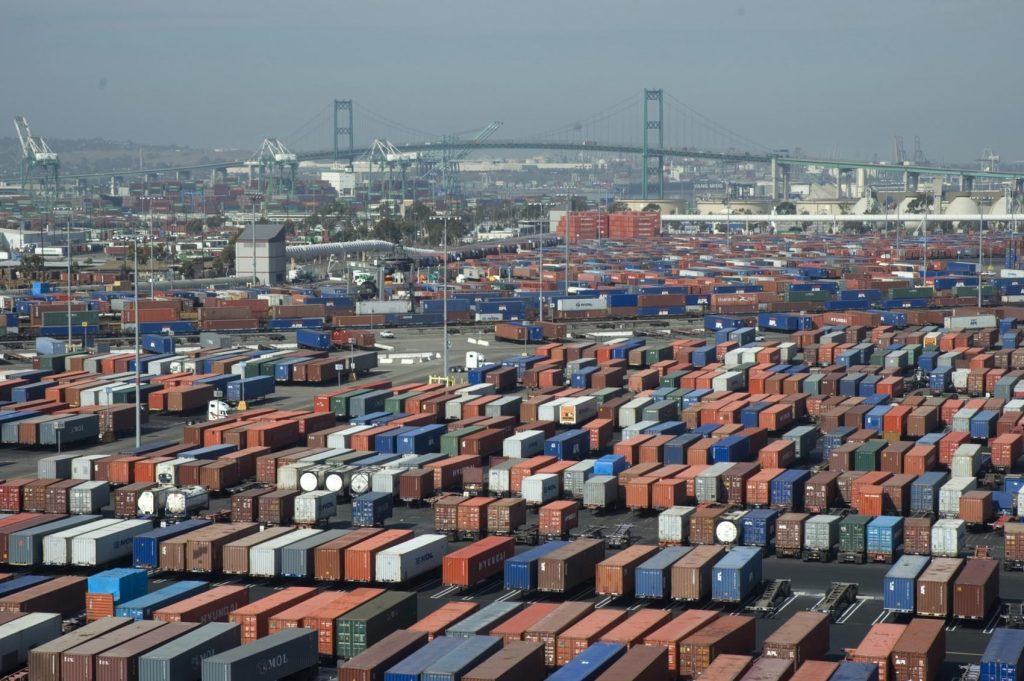
Bonanni’s innovative company, Sourcemap, helps clients visually map the supply chain route, from raw materials to end-users, providing unique and important visibility. Companies like Stoneyfield, Mars Chocolate, Fairphone, and Office Depot can see risks and disruptions in the supply chain in real time, act responsibly, promote sustainability, and please consumers who are increasingly curious and conscientious about materials sourcing.
The likes of the Wall Street Journal, Forbes, and The Guardian have taken interest in Dr. Bonanni and Sourcemap. Here he shares some insights with Fronetics on the growth of the company and how he won’t rest until mapping the supply chain is status quo.
What’s the most exciting thing going on at Sourcemap right now?
2015 is the year of supply chain mapping. When we started helping companies trace their products to the source, it was 2007 and the question was ‘why would we want to do that?’ Today it’s ‘how fast can we start?’ Whether it’s risk, sustainability, or simply finding more efficient ways to source products, companies need a big picture of the end-to-end supply chain. What’s exciting is how fast and far we help our clients get there – sometimes in as little as one day.
Tell me about how the maps are built. Are the maps on the free source platform built the same way as the maps on the enterprise platform?
Sourcemap started as a service for consumers to find out where products come from (free.sourcemap.com is still the only website where anyone can make a supply chain map, no training required). Users log in and map a supply chain – from raw material to end customer – as easily as drawing dots and lines on a Google map. Soon after the free website launched manufacturers approached us to see if we could help them figure out where their products come from. We had a lot of experience from serving millions of visitors through our free website, so we knew how to make a robust and intuitive interface for supply chain mapping. We adapted the technology to enterprise needs by adding company specific KPI’s, network analytics, and real-time reporting. The difference is that our enterprise users don’t draw the supply chains one link at a time. Their maps are automatically generated in near-real time from transportation, purchasing, and product lifecycle management databases.
Is it hard to convince businesses that there is an economic or competitive advantage to a utilizing a platform like Sourcemap?
It’s true that Sourcemap was originally built for sustainability, and it can be hard for companies to dedicate resources to long-term issues when short-term priorities come up every day. But our first success wasn’t helping companies be more sustainable in the long term. It was helping them tackle short-term crises, by developing a supply chain repository for emergency response and business continuity planning. Our clients were spending days and weeks to determine how a natural or human-made disaster was impacting any of thousands of suppliers worldwide. We brought that time down to minutes. Then supply chain managers started to see the benefit of knowing not just who they buy from, but who their suppliers buy from – and making decisions to consolidate or diversify supply, move inventories around, and decide when to in-source / out-source processes. These decisions represent huge savings in overall supply chain cost.
This is fantastic tool for companies who are proud of their supply chains, but what about those companies who aren’t, or who aren’t even fully aware of the steps and impact of their chain?
Over the years we’ve worked with companies big and small, with widely differing visibility into their supply chains. What we’ve seen is that the biggest benefit – the low-hanging fruits – are there for first-time supply chain mappers. These are companies that have expanded through acquisitions, are entering new markets or introducing new products – basically any organization that needs to account for a whole new way of doing business. Then, supply chain mapping is the easiest way to keep tabs on everyone in the supply chain and make sure that decisions are taken with an eye on the big picture.
In the years you’ve been doing this work have you seen a shift in consumer demand around the sourcing of materials and making of products? Is there increasing social pressure for companies to “do good”?
We’ve seen two drivers for supply chain sustainability and transparency: companies who want to attract the best talent, and brands looking to differentiate their product by providing information on its price, its composition, or its source.
Given that you teach at Columbia, I’m wondering if you see a difference in the passion, awareness, and attitude around sustainability with younger generations? Have you seen growth in the enrollment numbers in your classes?
I like to teach one or two evening classes a year (this Fall at NYU) to see how supply chain thinking is evolving as it becomes more mainstream. My class hasn’t changed much since it started in 2007, but the students have. Sustainability used to be a futuristic concern, and no one outside logistics departments ever talked about supply chains. Today there is a real desire among students to be social entrepreneurs, and part of that means thinking about products and services holistically – making sure that the social and environmental impacts are drivers of innovation, not just a nice-to-have. Enrollment has grown, and so has the number of departments where supply chains play a role: from engineering, architecture and design to business, public policy and international affairs.
Has social media played a role in the growth of the business and/or the operations of the business?
Sourcemap wouldn’t be here without social media. The fact that our supply chain maps can be embedded in other websites attracted over a million visitors in the first year. We saw brands embedding maps of their supply chains on their own websites, and we got a tremendous amount of traffic from being embedded and linked from the Huffington Post, Wired and Fast Company.
What are your ultimate goals for Sourcemap?
Supply chain mapping – knowing where products originate – gets easier the more companies do it. It requires information sharing, which means tighter collaboration between buyers and sellers. We’ve seen it become a requirement of purchasing departments: if you want to sell your products, disclose the raw material origins. That makes it easier to trust – and verify – the quality, the compliance, the sustainability of the product. Personally, I won’t rest until supply chain mapping becomes part of doing business as usual.
Dr. Leonardo Bonanni is Founder and CEO of Sourcemap, the supply chain mapping company. The New York-based startup offers enterprise software for companies to trace products, evaluate social, environmental and financial risks, and monitor improvements over time. One day soon you’ll be able to scan a product on a store shelf and be connected to the people who made it through the Sourcemap social network.
Leo is a supply chain transparency advocate named among the 100 Most Influential People in Business Ethics (2011) and America’s Most Promising Social Entrepreneurs (2012). He teaches sustainability at Columbia and at MIT, where he received his doctorate from the MIT Media Lab. He has a background as an architect, an inventor and a performer.
Fronetics Strategic Advisors is a leading management consulting firm. Our firm works with companies to identify and execute strategies for growth and value creation.
Whether it is a wholesale food distributor seeking guidance on how to define and execute corporate strategy; a telematics firm needing high quality content on a consistent basis; a real estate firm looking for a marketing partner; or a supply chain firm in need of interim management, our clients rely on Fronetics to help them navigate through critical junctures, meet their toughest challenges, and take advantage of opportunities. We deliver high-impact results.
We advise and work with companies on their most critical issues and opportunities: strategy, marketing, organization, talent acquisition, performance management, and M&A support.
We have deep expertise and a proven track record in a broad range of industries including: supply chain, real estate, software, and logistics.


by Elizabeth Hines | Jul 16, 2015 | Blog, Strategy

Remember the days when a rear-view mirror was all we needed to make business decisions? Now, predictive analytics appears poised to turn hindsight into a relic of the past.
Two Gartner analysts echo that sentiment, stating, “Few technology areas will have greater potential to improve the financial performance and position of a commercial global enterprise than predictive analytics.”
Executives are eager to jump on the bandwagon too. Although only 13% of 250 executives surveyed by Accenture said they use big data primarily for predictive purposes, as many as 88% indicated big data analytics is a top priority for their company. With an increasing number of companies learning to master the precursors to developing predictive models — namely, connecting, monitoring, and analyzing — we can safely assume the art of gleaning business intelligence from foresight will continue to grow.
Amid the promises of predictive analytics, however, we also find a number of pitfalls. Some experts caution there are situations when predictive analytics techniques can prove inadequate, if not useless.
Let’s consider three examples:
- Predictive analytics works well in a stable environment in which the future of the business is likely to resemble its past and present. But Harvard Business School professor Clayton Christensen points out that in the event of a major disruption the past will do a poor job of foreshadowing future events. As an example, he cites the advent of PCs and commodity servers, arguing computer vendors who specialized in minicomputers in the 1980s couldn’t possibly have predicted their sales impact, since they were innovations and there was no data to analyze.
- Bias in favor of a positive result is another danger when interpreting data; One of the most common errors in predictive analytics projects. Speaking at the 2014 Predictive Analytics World conference in Boston, John Elder, president of consulting firm Elder Research, Inc., made a good point when he noted that people “‘often look for data to justify our decisions, when it should be the other way around.”
- Mining big data will further do little good if the insights are not directly tied to an operational process. I’ve a feeling more companies than we realize are wasting precious time and manpower on big data projects that are not adequately understood, producing trivia rather than actionable business intelligence.
With the above challenges in mind, talent acquisition and thorough A/B tests will be key components of any predictive analytics project. What else do you think organizations need to do to use foresight effectively?
You may also be interested in:
Fronetics Strategic Advisors is a leading management consulting firm. Our firm works with companies to identify and execute strategies for growth and value creation.
Whether it is a wholesale food distributor seeking guidance on how to define and execute corporate strategy; a telematics firm needing high quality content on a consistent basis; a real estate firm looking for a marketing partner; or a supply chain firm in need of interim management, our clients rely on Fronetics to help them navigate through critical junctures, meet their toughest challenges, and take advantage of opportunities. We deliver high-impact results.
We advise and work with companies on their most critical issues and opportunities: strategy, marketing, organization, talent acquisition, performance management, and M&A support.
We have deep expertise and a proven track record in a broad range of industries including: supply chain, real estate, software, and logistics.


by Elizabeth Hines | Jul 15, 2015 | Blog, Leadership, Strategy, Supply Chain
 The sharing of tangible and intangible assets will increasingly become a fundamental feature of successful businesses.
The sharing of tangible and intangible assets will increasingly become a fundamental feature of successful businesses.
Few developments of late are as intriguing as the rise and disruptive impact of the collaborative economy. In a very short time, services that we may have thought of as permanent fixtures of our business and personal lives have been rendered obsolete by the sudden sharing of tangible and intangible assets in the peer-to-peer, business to consumer (B2C), and business to business (B2B) spheres.
B&B and hostels, car rental, and DVD rental are giving way to peer-to-peer accommodations, car sharing, and music and video streaming. The Marriott Hotel chain used the online platform LiquidSpace to convert empty conference rooms into rentable work spaces for guests as well as outside visitors. Walgreens teamed up with TaskRabbit, an online marketplace for outsourcing errands, to deliver products during flu season. The list is endless.
Rachel Botsman, an innovation strategist who has spent the past four years studying 500 collaborative economy startups worldwide, concludes in Harvard Business Review:
The real power of the collaborative economy is that it can serve as a zoom lens, offering a transformative perspective on the social, environmental, and economic value that can be created from any of a number of assets in ways and on a scale that did not exist before. In that transformation lie threats—and great opportunities.
While consumer sharing may have received the most media attention, Robert Vaughan, an economist at PwC Strategy & Inc., argues the open sharing of resources among businesses may present an even larger opportunity. Although, on the surface, it seems like an unlikely marriage – businesses do compete, after all – a growing number of successful collaborations prove Vaughan is right.
He writes:
In just a few years of activity, it has become clear that the unfettered exchange of otherwise unused major assets, including physical space and industrial equipment, allows a sharing company to operate more efficiently than its non-sharing rivals. Companies that go further still, wholeheartedly embracing the sharing of less tangible assets, may benefit from a different sort of change, one involving their culture, that builds new types of connections with, and sensitivity to, the world outside.
One example of an interesting collaboration involves General Electric and Quirky, an online inventor community. GE and other market giants such as IBM and Samsung file thousands of patents every year, most of which never move beyond the drawing board. The collaboration gives Quirky open access to GE’s patents, allowing for products that normally would not have been put to productive use – such as a smartphone controlled window air conditioner – to be brought to market.
Sometimes a direct collaboration may not even be necessary. A company may choose to place an undeveloped product on an online technology exchange, thereby opening itself to the possibility of building a connection to another company with complimentary expertise.
In many respects, enterprise sharing is still in its infancy and is likely to evolve just like Airbnb, whose concept seemed “fringe” when it launched in 2008 (it was initially marketed as a service for people to stay the night on their air beds in strangers’ homes). Now the company has amassed more than 650,000 rooms in 192 countries and threatens to disrupt not only the hotel industry but the entire hospitality sector.
Fronetics Strategic Advisors is a leading management consulting firm. Our firm works with companies to identify and execute strategies for growth and value creation.
Whether it is a wholesale food distributor seeking guidance on how to define and execute corporate strategy; a telematics firm needing high quality content on a consistent basis; a real estate firm looking for a marketing partner; or a supply chain firm in need of interim management, our clients rely on Fronetics to help them navigate through critical junctures, meet their toughest challenges, and take advantage of opportunities. We deliver high-impact results.
We advise and work with companies on their most critical issues and opportunities: strategy, marketing, organization, talent acquisition, performance management, and M&A support.
We have deep expertise and a proven track record in a broad range of industries including: supply chain, real estate, software, and logistics.


by Fronetics | Jul 14, 2015 | Blog, Logistics, Manufacturing & Distribution, Strategy, Supply Chain

To see lean perfected – study the NASCAR pit. In a matter of seconds, the pit crew has changed tires, wiped down the windshield, filled up fuel, and given the driver a drink of water. Everything is in the right place at the right time. If only every distribution center would run that smoothly. What’s clear is that mastering inventory levels is central to the equation of eliminating waste, but inventory management is becoming a vexing problem for some organizations – compounded by multi-channel distribution, inadequate demand forecasting, and a lack of communication among appropriate parties.
Taking a closer look at the experiences of forerunner companies in their quests to master lean inventory management might just help your company avoid these top three snags.
Failure to Adapt Business Processes
In an effort to reduce merchandise sitting around on warehouse racks, some organizations take lean too far. The problem, in this case, is one of business process rather than software. While management sees the financial impact of cutting inventory, they tend to pay less attention to how it will affect operations. The heads of distribution quite frequently are not even invited to take part in the decision and find out only when fewer cases and pallets show up at receiving. Adapting business processes to involve the managers of procurement, finance, operations, and sales and marketing, is key to maximizing efficiency. In other words, open up the silo by building it in to your formal and informal processes.
Failure to Collaborate
Even with sophisticated demand forecasting models on hand, input from all parties is needed for an accurate assessment of inventory levels. And although demand forecasting can help an organization plan around high-level “what if” scenarios, it may not always be able to break it down on a granular level or take into account the increasing number of variables associated with multi-channel distribution. Collaboration is crucial.
Failure to Align Objectives
Sometimes the answer to the issue of inventory levels is counterintuitive. Even with lean as the driving force, the notion of optimization cannot be left out. In some instances, it makes sense to increase rather than minimize inventory if it will contribute to lowering your overall supply chain costs. Your business and inventory strategies need to align.
Despite the fact that in recent years the lean revolution has hit manufacturing, many organizations, especially retailers and wholesalers, have yet to apply lean principals. And among those who do dabble in lean, the focus tends to be on suppliers upstream rather than adding value to the end customer. As more and more businesses seek to tighten the management of their inventory in order to increase efficiencies, opportunities to address end customer value will emerge. Paul A. Myerson, professor in supply chain management, identifies store- and distribution operations as prime candidates since that’s where the most waste can be cut. He writes:
Distribution is all about optimizing the trade-offs between handling costs and warehousing costs, and maximizing the warehouse’s total cube—utilizing its full volume, while maintaining low materials handling costs and minimizing travel time.
Mastery of lean management principals will come for companies that are both successful in identifying new efficiency opportunities within their existing supply chain and navigating around the pitfalls of businesses that have instituted similar inventory management techniques.
Fronetics Strategic Advisors is a leading management consulting firm. Our firm works with companies to identify and execute strategies for growth and value creation.
Whether it is a wholesale food distributor seeking guidance on how to define and execute corporate strategy; a telematics firm needing high quality content on a consistent basis; a real estate firm looking for a marketing partner; or a supply chain firm in need of interim management, our clients rely on Fronetics to help them navigate through critical junctures, meet their toughest challenges, and take advantage of opportunities. We deliver high-impact results.
We advise and work with companies on their most critical issues and opportunities: strategy, marketing, organization, talent acquisition, performance management, and M&A support.
We have deep expertise and a proven track record in a broad range of industries including: supply chain, real estate, software, and logistics.


by Elizabeth Hines | Jul 13, 2015 | Big Data, Blog, Data/Analytics, Strategy, Supply Chain

Analytics is good for business — as long as you can make sense of it.
Does your business suffer from a case of data overload? Or do you steer clear of new investments in supply chain analytics because you are afraid they could yield more data than your business can handle? You are in good company.
Several recent surveys indicate companies either are wary of advanced analytics tools or say they have failed to leverage the technology. The issue does not seem to be a lack of knowledge of its existence or potential impact — end users are generally well informed — but how to absorb the data effectively and apply it across the entire organization.
According to a Telematics Update, for example, vendors would be wise to spend less time on their sales pitch and more time presenting the data in a digestible format, ensuring compatibility with the end user’s legacy systems, and aligning the solution with the end-user’s key performance indicators.
The challenge is also captured in an Accenture survey in which only one in five companies said they are “very satisfied” with the returns they have received from analytics. And it’s not for lack of trying. Two-thirds of companies have appointed a chief data officer in the last 18 months to oversee data management and analytics, while 71 percent of those who have not created such a position plan to do so in the near future.
This passage from Accenture’s survey report hits the nail on the head:
Companies wanting to compete more aggressively with analytics will move rapidly to industrialize the discipline on an enterprise-wide scale, redesigning how fact-based insights get embedded into key processes, leading to smarter decisions and better business outcomes.
Most organizations measure too many things that don’t matter, and don’t put sufficient focus on those things that do, establishing a large set of metrics, but often lacking a causal mapping of the key drivers of their business.
As the survey suggests, the move away from an isolated approach to an integrated cross-functional model may be the key to squeezing the most out of supply chain analytics. According to Deloitte, the key to delivering strategic insights is creating asingle authoritative data set from which all business units can draw information.
However, only 33% of the Accenture survey respondents said they are “aggressively using analytics across the entire enterprise.” Instead, highly customized data is often collected for units within the organization. A spending forecast by procurement may look nothing like its counterpart coming out of logistics. The inconsistency in reporting makes it hard to share the knowledge, and that takes us back to square one: lots of data and little useful information.
Jerry O’Dwyer, a principal with Deloitte Consulting, summed it up this way in a 2012 post:
If you are performing analytics in different areas of the supply chain — for example, spend analytics or demand planning — you may be missing opportunities that an expansive approach can yield. For companies of all kinds, in-depth supply chain analysis offers an opportunity to create increased value throughout their operations.
Let’s hear it: What do you think companies need to do to put analytics to effective use?
Fronetics Strategic Advisors is a leading management consulting firm. Our firm works with companies to identify and execute strategies for growth and value creation.
Whether it is a wholesale food distributor seeking guidance on how to define and execute corporate strategy; a telematics firm needing high quality content on a consistent basis; a real estate firm looking for a marketing partner; or a supply chain firm in need of interim management, our clients rely on Fronetics to help them navigate through critical junctures, meet their toughest challenges, and take advantage of opportunities. We deliver high-impact results.
We advise and work with companies on their most critical issues and opportunities: strategy, marketing, organization, talent acquisition, performance management, and M&A support.
We have deep expertise and a proven track record in a broad range of industries including: supply chain, real estate, software, and logistics.










