by Fronetics | Aug 6, 2014 | Blog, Logistics, Marketing, Social Media, Strategy, Supply Chain, Transportation & Trucking
Keychain Logistics has made two bold promises. The company has promised truckers that they will never drive empty again and has promised shippers that Keychain will improve their bottom line.
Can the company deliver on these promises?
Who is Keychain Logistics?
Keychain is a leading transportation provider enabling businesses to directly engage carriers, track shipments, and monitor its logistics needs online.
According to Bryan Beshore, the company’s founder, Keychain grew out of the idea that a technology driven marketplace could operate with significantly lower overhead than a manual, human powered brokerage:
“My initial contact with the industry was in 2000. I have researched, analyzed, and thought about the industry ever since. Keychain is a product in understanding the fundamental efficiency problems the third party logistics industry has faced for a long time.”
Beshore goes on to point out that while building a technology company is tough, building Keychain was easier than anticipated:
“With Keychain it was a natural process and easier than I had imagined. I believe the reason for this is twofold: the challenges this industry faces are huge, and the solutions we are building to meet those problems are really fun to solve. Because our work directly affects the wallets of our users (increased pay for drivers, better rates for shippers), we are effectively helping people create better lifestyles for themselves and their families, and that’s really rewarding.”
The company was slated to be built in 2007; however, the timing was not right given the low proliferation of internet-connected mobile devices (500 million). Beshore waited. In 2012 he decided to move forward with the launch of the company (the number of internet connected devices reached 8.7 billion in 2012).
How does it work?
One can draw a parallel between Keychain and Uber – the company removes the broker and connects truckers directly with shippers therefore enabling truckers to focus on driving and shippers to focus on selling products.
Keychain is a marketplace for truckers to book commercial shipments directly with shippers. The company’s technology matches owner operator drivers (and small fleets) with shippers who rely on Keychain Logistics to find the ideal carrier for their freight.
The core of the company’s platform is their network of ten-of-thousands of carriers throughout the US who are connected 24/7/365 via Keychain’s iOS, Android, and Windows phone apps. Keychain can instantly communicate load opportunities to independent owner-operators, 97 percent of whom operate in fleets of 20 trucks or less, and small carrier fleets.
Too good to be true?
One of the biggest challenges the company has faced is that it is perceived as being “too good to be true.” Beshore:
“The transportation industry is traditional and technologically far behind. Because of this, the inherent challenge to sharing our offering is overcoming the “too good to be true” bias. While many of our potential customers have wanted a product like ours for a while, they either don’t know how to articulate it in a Google search or are skeptical that tech companies like Keychain are committed to solving their problems.”
Solving immediate need
Keychain has been working to overcome the perception of being too good to be true. It has been talking to current users, and has honed in on developing a solid marketing message. The message – we can solve your immediate need.
Not expressing the full-vision up front has been a challenge when Keychain reaches out to companies with whom they have little or no relationship; however, they have found that solving an immediate need is what gets companies excited.
What immediate need(s) can the company address? According to Beshore: “For shippers, this is getting them access to trucks, sometimes within just minutes of our first contact. For drivers, this means getting them a paying load when they’re stuck at a rest stop, are far from home, or simply need a line-haul out.”
Leveraging social media to grow the company
The company has found that one of the best ways to use social media is for listening. Rather than spend time and money putting together and distributing sales literature, the company searches for relevant industry hashtags (i.e.: #trucking) to see what people are talking about, and more importantly what they care about. By using social media this way, Keychain is an audience to users instead of the other way around. This has enabled the company to shape their offering with a solid understanding of what people want from a transportation provider.
“From phone calls to interviews, crowdfunded campaign partnerships, and beyond, social media has certainly helped us grow our business,” says Beshore.
Can they deliver?
Can Keychain deliver on their bold promises? Their customers believe so. Here is what three customers say about the company:
“With Keychain I no longer have to waste hours on logistics. Their platform makes it easy to quickly enter shipment details and receive the most competitive rates available.” Marc DeVidts, Double Robotics
“Keychain gives us instant access to thousands of reliable carriers nationwide. It’s the most efficient and cost effective tool we’ve found.” Nathan Brown, Reclaimed American Hardwood
“Within minutes I can enter my shipment details and Keychain handles the rest. Annoying phone calls and exorbitant broker fees are over.” Ad Sachan, Treeline Woodworks.

by Fronetics | Aug 6, 2014 | Blog, Logistics, Marketing, Social Media, Strategy, Supply Chain, Transportation & Trucking

Keychain Logistics has made two bold promises. The company has promised truckers that they will never drive empty again and has promised shippers that Keychain will improve their bottom line.
Can the company deliver on these promises?
Who is Keychain Logistics?
Keychain is a leading transportation provider enabling businesses to directly engage carriers, track shipments, and monitor its logistics needs online.
According to Bryan Beshore, the company’s founder, Keychain grew out of the idea that a technology driven marketplace could operate with significantly lower overhead than a manual, human powered brokerage:
“My initial contact with the industry was in 2000. I have researched, analyzed, and thought about the industry ever since. Keychain is a product in understanding the fundamental efficiency problems the third party logistics industry has faced for a long time.”
Beshore goes on to point out that while building a technology company is tough, building Keychain was easier than anticipated:
“With Keychain it was a natural process and easier than I had imagined. I believe the reason for this is twofold: the challenges this industry faces are huge, and the solutions we are building to meet those problems are really fun to solve. Because our work directly affects the wallets of our users (increased pay for drivers, better rates for shippers), we are effectively helping people create better lifestyles for themselves and their families, and that’s really rewarding.”
The company was slated to be built in 2007; however, the timing was not right given the low proliferation of internet-connected mobile devices (500 million). Beshore waited. In 2012 he decided to move forward with the launch of the company (the number of internet connected devices reached 8.7 billion in 2012).
How does it work?
One can draw a parallel between Keychain and Uber – the company removes the broker and connects truckers directly with shippers therefore enabling truckers to focus on driving and shippers to focus on selling products.
Keychain is a marketplace for truckers to book commercial shipments directly with shippers. The company’s technology matches owner operator drivers (and small fleets) with shippers who rely on Keychain Logistics to find the ideal carrier for their freight.
The core of the company’s platform is their network of ten-of-thousands of carriers throughout the US who are connected 24/7/365 via Keychain’s iOS, Android, and Windows phone apps. Keychain can instantly communicate load opportunities to independent owner-operators, 97 percent of whom operate in fleets of 20 trucks or less, and small carrier fleets.
Too good to be true?
One of the biggest challenges the company has faced is that it is perceived as being “too good to be true.” Beshore:
“The transportation industry is traditional and technologically far behind. Because of this, the inherent challenge to sharing our offering is overcoming the “too good to be true” bias. While many of our potential customers have wanted a product like ours for a while, they either don’t know how to articulate it in a Google search or are skeptical that tech companies like Keychain are committed to solving their problems.”
Solving immediate need
Keychain has been working to overcome the perception of being too good to be true. It has been talking to current users, and has honed in on developing a solid marketing message. The message – we can solve your immediate need.
Not expressing the full-vision up front has been a challenge when Keychain reaches out to companies with whom they have little or no relationship; however, they have found that solving an immediate need is what gets companies excited.
What immediate need(s) can the company address? According to Beshore: “For shippers, this is getting them access to trucks, sometimes within just minutes of our first contact. For drivers, this means getting them a paying load when they’re stuck at a rest stop, are far from home, or simply need a line-haul out.”
Leveraging social media to grow the company
The company has found that one of the best ways to use social media is for listening. Rather than spend time and money putting together and distributing sales literature, the company searches for relevant industry hashtags (i.e.: #trucking) to see what people are talking about, and more importantly what they care about. By using social media this way, Keychain is an audience to users instead of the other way around. This has enabled the company to shape their offering with a solid understanding of what people want from a transportation provider.
“From phone calls to interviews, crowdfunded campaign partnerships, and beyond, social media has certainly helped us grow our business,” says Beshore.
Can they deliver?
Can Keychain deliver on their bold promises? Their customers believe so. Here is what three customers say about the company:
“With Keychain I no longer have to waste hours on logistics. Their platform makes it easy to quickly enter shipment details and receive the most competitive rates available.” Marc DeVidts, Double Robotics
“Keychain gives us instant access to thousands of reliable carriers nationwide. It’s the most efficient and cost effective tool we’ve found.” Nathan Brown, Reclaimed American Hardwood
“Within minutes I can enter my shipment details and Keychain handles the rest. Annoying phone calls and exorbitant broker fees are over.” Ad Sachan, Treeline Woodworks.
by Jennifer Hart Yim | Jun 26, 2014 | Blog, Internet of Things, Logistics, Manufacturing & Distribution, Marketing, Social Media, Strategy, Supply Chain

This article is part of a series of articles written by MBA students and graduates from the University of New Hampshire Peter T. Paul College of Business and Economics.
Supply Chain Management will use the Internet of Things to improve factory workflow, increase material tracking, and optimize distribution to maximize revenues.
“Clap on “(clap, clap), “Clap off” (clap, clap), “the Clapper”!!
When introduced in 1986, “The Clapper” light switch was considered a significant breakthrough in home automation. Today, with advances in communication, sensors, and internet-connected devices, you can change the temperature of your home, your lights, appliances, and security system all from your smartphone — from anywhere in the world. This is just one simple example in the growing “Internet of Things” technology. The potential is enormous, not just in home automation but in industrial applications like manufacturing and distribution.
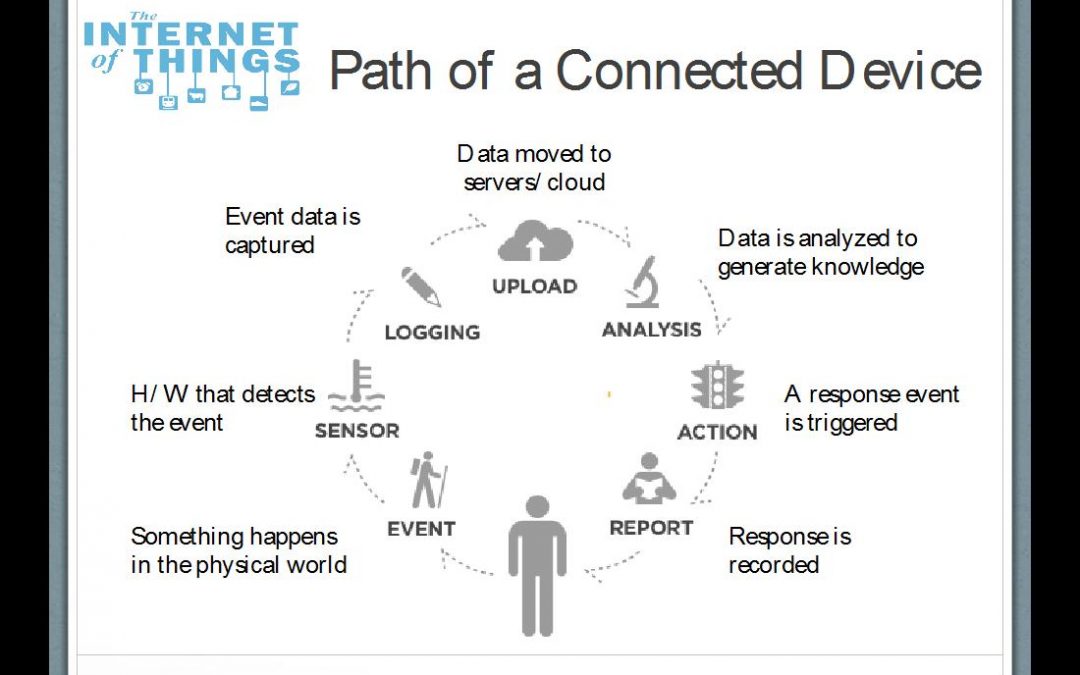
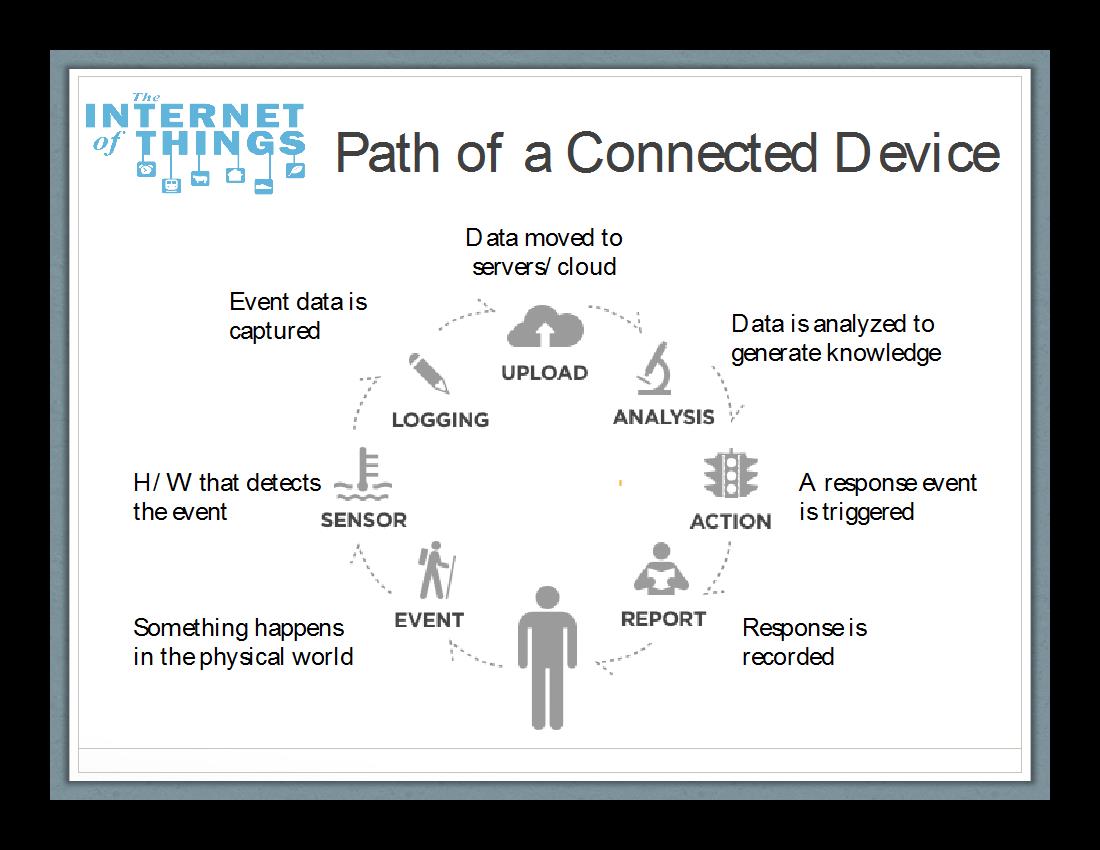
The Internet of Things (IoT) is broadly defined as the merging of the physical and digital worlds. It’s a scenario in which people and/or objects can be uniquely identified with the ability to share information over a network without any actual conscious intervention. The data is automatically transferred, analyzed, and used to trigger an event. Figure 1 below demonstrates how one of these devices functions and interacts with the Internet and other devices.
Figure 1.
The IoT and Supply Chain Management
While many of us may be familiar with recent advancements in home automation, like the Nest thermostat, the real impacts of IoT will be in Supply Chain Management. Recent reports by Cisco, IDC and Gartner all claim that a significant increase in the number of devices making up the Internet of Things will have a profound impact on how future supply chains will operate. The 2011 Cisco report predicts there will be 50 billion connected devices globally by 2020, or about 6.5 devices for each person, up from only approximately 2.5 today (see figure 2). More active devices means more available data — to the point where they will be ubiquitous and transparent in our every day lives.
Figure 2.
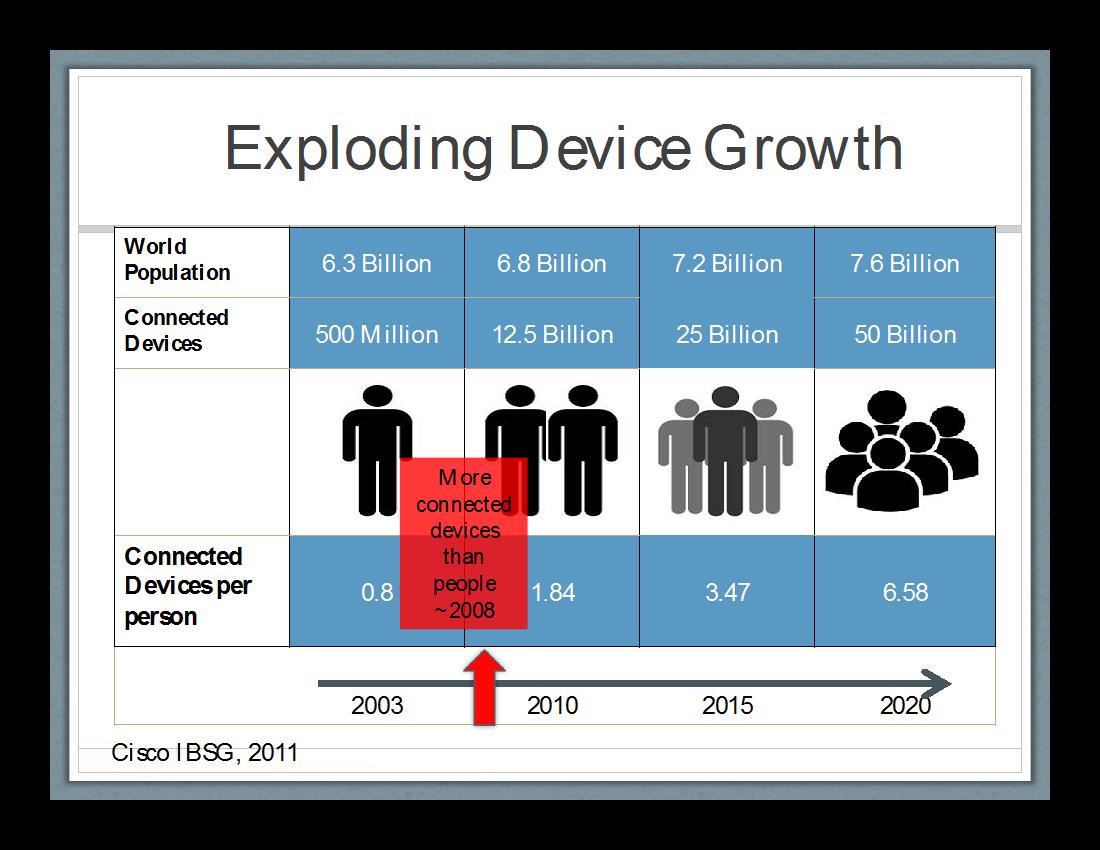
Impacts to supply chain will be broad and far-reaching, utilizing Big Data to gather and analyze information across the entire process.
Some IoT devices have been in place for some time, such as commercial telematics now used in trucking fleets to improve logistics efficiency. Other commercial type applications — like fabrics that use sensors within clothing and industrial fabrics to monitor human health or manufacturing processes — are just being developed now.
Mark Morely of GSX, a leading provider of monitoring and management solutions, recently discussed three key impacts he believed IoT would have on the Supply Chain industry: Pervasive Visibility, Proactive Replenishment, and Predictive Maintenance. This is a great way to explain the immediate benefits, so I will summarize Mark’s description and expand with some real-world examples.
Three key impacts the IoT will have on the supply chain industry
1) Pervasive Visibility
Mark describes this as the ability to track and monitor a shipment in real time using a combination of sensors (RFID), connected devices, and communication channels (3G/4G, GPS, internet). It provides the ability to have real-time transit status, including location, temperature, and diagnostics — far more information than legacy infomatics provided.
One great example I found is from a company called Purefresh, who are at the cutting edge of Supply Chain IoT technology. They offer not only real-time shipment condition tracking, but also the ability to model and develop transit routes to optimize freshness in perishable cargo — taking into account environmental elements, such as ozone, atmospheres, and temperature. They indicate that an estimated “30% to 50% (or 1.2-2 billion tons) of all food produced on the planet is lost before reaching a human stomach.” IoT advancements will not only better optimize transit flow but also better serve humanity.
2) Proactive Replenishment
It’s the capability to automatically recognize the need to order and restock a product on a “machine-to-machine” basis, reducing the need for human interaction. The most common example is that vending machines will know when it’s out of or low on a Snickers bars and immediately trigger an alert to reorder them, instead of waiting for a service person to check on the vending machine and reorder products manually. The result is less human intervention, quicker replenishment, better sales forecasting and ultimately increased revenues. Oh, and many more happy office workers who really need a mid-afternoon sugar rush!
Opportunities for this technology go far beyond the candy vending machine though. Industries with time critical inventories like hospitals and pharmacies can better maintain supplies by supplementing human inventory control with real time use tracking. A much less critical but more broadly used application comes from Coke’s Freestyle fountain soda machine. It’s about the same size as the existing vending machines but it can dispense 126 kinds of flavors, offering an almost infinite amount of combinations. It uses Radio Frequency ID (RFID) cartridges that store the concentrated syrups in the machine. The RFID chips detect how much of each syrup it has and what combinations are being used. When it detects that it needs supplies, it transmits the information to both Coca-Cola and the storeowner including what has been sold, a record of when sales occurred, troubleshooting information, and service data. As a result, soda sales and customer satisfaction increases, all with less effort by the storeowner.
3) Predictive Maintenance
This application is closer to the true machine-to-machine communications the IoT was intended for. From large-scale manufacturing to diagnostics on the family minivan, predictive maintenance utilizes sensors and connected devices to monitor and react to issues. This self-diagnosis capability can detect a potential issue before there’s a failure, order a replacement part, and even schedule maintenance to avoid costly downtime.
Not only does predictive maintenance help keep factories running longer and the family minivan from unexpectedly breaking down, it can improve efficiency throughout the whole supply chain. If equipment manufacturers constantly receive service data from factory equipment, they can better trend problems and focus on those issues for future products. Parts depots can better forecast inventories and determine consistent safety stock levels. IoT, in this example, is a true B2B (business to business) — automating the communication between businesses on every link of the chain.
In relation to home automation, predictive maintenance will become integrated into our everyday lives. Appliances will become smarter, more efficient, and easier to monitor. Internet-connected sensors will be embedded into everything from refrigerators to washers/dryers and HVAC systems. So much so that companies like GE are investing heavily into these technologies, in both commercial and industrial applications. These connected appliances will perform self-diagnosis, determine the most cost-efficient time to operate, and even automatically order maintenance parts like furnace filters when needed. Imagine getting an alert on your smartphone that your forced hot air furnace needs a new air filter, and it has already been ordered through your Amazon account. It just saved you effort in remembering to check the filter and ordering it — leading to a cleaner, longer-lasting, and more efficient furnace.
So, why isn’t IoT here yet?
It’s close but there are still hurdles to overcome. In recent years, advances in sensor technologies, 4G communications, and cloud computing has made achieving Internet of Things capabilities even more possible. But for companies in the Supply Chain to leverage these opportunities, they will need to expand investment into cloud-based platforms that can support scalable devices and data-analysis services.
Critical to IoT’s success will be the necessary “middleware” software communication protocols to link all these devices. Companies like ProSyst and open-source SW projects like OPENIoT are pioneering these capabilities. But even with this progress, agreements on industry standards will be key to long-term platform success.
Having a common IoT protocol will be necessary to link the physical and digital worlds on a consistent and economical basis. Understanding the need for standards and common architectures, Intel has led the way by recently creating the not-for-profit Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC) with other vested companies like AT&T, Cisco, GE, and IBM. The connected Supply “Chain” will become exponentially longer once these common standards are in place.
The Internet of Things trend is quickly approaching and will impact the way we live and work through increased productivity and efficiency. Supply Chain Management will continue utilizing these advanced technologies to improve factory workflow, increase material tracking, and optimize distribution to maximize revenues.
In 1986, I recall how innovative I thought the Clapper was — I couldn’t have imagined how connected we would become only 28 years later. And the next 28 will be sure to amaze.
Steve Mondazzi is a Principal Master Planner in the Defense Contracting industry. After 20 years’ experience in project management and schedule development, he decided to further his education by recently earning a Masters in Technology Management at the University of New Hampshire. He’s a certified PMI Project Management Professional, an entrepreneur, and an avid lover of all things technology. He currently resides in Massachusetts with his wife, two teenagers, and an excessive collection of headphones. Steve can be contacted via his Twitter account @schedulepro or through LinkedIn.
Related posts:

by Fronetics | Jun 24, 2014 | Blog, Logistics, Marketing, Social Media, Strategy
Many companies within the logistics and supply chain industries are stuck on the social media starting line. The reason – “they can’t get past the word ‘social’ and the perception it creates.” The reality is that social media is a tool that can be utilized to create value and grow your business.
This is the fifth in a series of articles that provides examples of companies within the logistics and supply chain industries who have moved beyond the social media starting line and have realized the business value of participating in social media.
Logistics industry start-ups leverage social media
Social media allows for instant connections and communication. Two start-ups, Trucker Path and Keychain Logistics, have created solutions for the logistics industry which leverage these characteristics of social media.
Trucker Path
Launched in February 2013, Trucker Path is a mobile platform for the trucking industry which connects shippers and carriers, and provides crowdsourced logistical assistance.
Specifically, the Trucker Path app (available via iOS, Andriod, and Web) enables carriers to find truckloads, shippers to move their cargo, and for truckers to get crowdsourced logistical information such as the locations of truck stops, rest areas, and information on weigh stations.
Keychain Logistics
Keychain Logistics uses technology to automate the marketplace and match shippers with carriers.
The Keychain Logistics app (available via iOS, Andriod, and Web) provides instant communication between shippers and carriers – eliminating the need for human powered brokerage.
Both Trucker Path and Keychain Logistics have recognized that there is more to social media than socializing – they have recognized that social media is a business tool.
by Fronetics | Jun 23, 2014 | Blog, Logistics, Marketing, Social Media, Strategy, Supply Chain
Many companies within the logistics and supply chain industries are stuck on the social media starting line. The reason – “they can’t get past the word ‘social’ and the perception it creates.” The reality is that social media is a tool that can be utilized to create value and grow your business.
This is the fourth in a series of articles that provides examples of companies within the logistics and supply chain industries who have moved beyond the social media starting line and have realized the business value of participating in social media.
Cerasis is a top freight logistics company and truckload freight broker. During the company’s first 15 years it focused on traditional sales and marketing strategies and relied heavily on referrals. This strategy worked. Cerasis acquired new customers, retained current customers, and realized positive growth. However, Cerasis was not viewed as an industry leader, and brand awareness was low.
In 2012 Cerasis decided to participate in social media and launch a content marketing strategy.
Cerasis began actively blogging, and began using Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, Pinterest, and Google+. The company quickly became seen as a leader within the industry, and brand awareness increased dramatically.
Within 15 months the company received 71 leads from search engines, 65 leads from social media, and 52 leads from webinars. Even more impressive, within 15 months the company gained 35 customers (one customer within the freight logistics industry can mean a lot of revenue).
The results show that Cerasis is no longer on the social media starting line – rather, Cerasis is now a leader, not only in the freight logistics industry, but also in using social media as a business tool.

by Jennifer Hart Yim | Jun 19, 2014 | Blog, Logistics, Manufacturing & Distribution, Strategy, Supply Chain

Entrants to the market need to understand the barriers to entry and problems with management and transparency within the pet food industry supply chain.
This article is part of a series of articles written by MBA students and graduates from the University of New Hampshire Peter T. Paul College of Business and Economics.
The pet food industry is a market that boasts $21.57 billion dollars in sales in the United States (2013). With 95.6 million cats and 83.3 million dogs owned in the United States, it is no wonder that there is such a large market for the food that the self-proclaimed “pet parents” feed them. However, it isn’t all good news for aspiring entrants, as they must first understand the supply chain that dictates this growing industry.
To manufacture, or not to manufacture
When a pet food company chooses to produce a product, they essentially have three options: 1) manufacture it themselves, or choose a co-packer who will either 2) use a private label or 3) manufacture the food to the specifications of the brand.
A contract packer (co-packer), otherwise known as a contract manufacturer, is a company that manufactures and packages foods for their clients. The manufacturer works under a contract with the hiring company to manufacture the pet food as though the hiring company was doing it themselves.
Co-packers can manufacture several different brands and for several companies at once. An example of a co-packer would be C.J. Foods, Inc. with manufacturing plants in Bern, Kansas, and The Pawnee City, Nebraska. According to C.J. Foods Inc., the company produces over 300 varieties of animal foods, including dog, cat, reptile, and exotic bird.
Companies typically outsource to another entity for production due to cost savings, rather than building their own plant. Additionally, they can focus on their own core competence, whether it is marketing, sales, etc. The manufacture’s core competency is production, and they have the experience and knowledge to produce the pet foods already. However, there can be many challenges associated with the management of pet food supply chains and co-packers in particular.
The challenges with co-packers
As the pet food market grows and becomes more complex, the sourcing of ingredients becomes more complicated.
Foreign suppliers source products from numerous small farms, and identities become lost and commingled. Unfortunately, brands are relying on these suppliers to meet food-safety criteria.
Additionally, these brands typically rely on audits of suppliers by private third-party companies that carry no guarantee. An example of this would be Kellogg and Peanut Corporation of America (PCA). Kellogg had PCA audited by AIB international, and PCA passed with a superior rating. However after the recall (explained in detail below), the FDA found leaks and rodent infestations within the plant.
Pet food industry product recalls
There have been two major recalls within the pet food industry in recent years.
One, the largest in history, was the ChemNutra recall in 2007. Two Chinese export firms sold wheat gluten bags tainted with melamine to Las Vegas-based ChemNutra, “the Chinese ingredient specialist importer.” ChemNutra then sold the tainted wheat gluten to pet food makers under false certificates of analysis. As a result, 5,300 pet foods were recalled, and thousands of cats and dogs were injured/killed. Owners of both the Chinese companies and ChemNutra pleaded guilty to various misdemeanors involving the mis-branding of food and conspiracy to commit wire fraud.
The second recall involves a 2009 salmonella outbreak in the Peanut Corporation of America’s plant in Blakely, Georgia. PCA knowingly shipped salmonella-tainted products across the country to many manufacturers, including those in the pet food industry. Along with the shipments, they sent certificates of analysis that indicated the product contained no salmonella, but they had yet to receive the test results (which were positive). This resulted in 3,200 pet food products being recalled, 8 deaths, and 500 illnesses. A 76-count indictment charged four former officials at PCA with numerous infractions relating to salmonella-tainted peanuts and peanut products.
These two examples are the horrific results from a lack of control over the supply chain within the manufacturing of pet foods. The consequences of these recalls, first and foremost, can cause the injury and death of both pets and people. Beyond that, there is implicit lost brand trust, consumer demand decrease, headaches for retailers/wholesalers, and severe cost increases for the company.
Solution: Improving supply chain management
Given the information above, it is essential that companies proactively work to avoid recalls through better management of the supply chain.
Co-packers become problematic when an ingredient or plant is infected because that trickles down to the many different brands and companies for whom they manufacture. That is not to say that pet food companies should never use a co-packer, especially because the cost-saving benefits can be so great. Pet food companies, however, should do their research prior to choosing a co-packer.
If you are using a private label, know where the co-packer is sourcing its ingredients. If you are not using a private label, you need to ensure you know the suppliers with whom the co-packer is working. The same rule applies if your pet food company has its own manufacturing plant, as well.
Secondly, pet food manufacturers can supplement third-party audits of co-packers’ plants with their own inspection and testing of ingredients and plant surfaces.
As a consumer purchasing these foods off the shelf, attempt to do your research, too. Although you may not be able to see exactly where products are coming from due to confidentiality of competitive sourcing, you can choose brands that have a commitment to transparency and educating the consumer on where their ingredients are sourced from. An example of this would be Natura Pet Products, which launched its “See Beyond The Bag” campaign. This part of their interactive website allows consumers to click on any product and view where in the world any specific ingredient in the product is being sourced from. Additionally, consumers can educate themselves on how Natura ensures a quality manufacturing process.
In conclusion, pet food manufacturing can be a difficult industry if a company is not well versed in the associated challenges. If a tight reign is held over the supply chain and quality manufacturing follows, the pet food industry is a growing market with a bright outlook for companies vying to do business within it.
Mikayla Cadoret recently completed her MBA at the University of New Hampshire – Paul College of Business and Economics. She is an experienced sales representative and is interested in pursuing a career in marketing or supply chain management. She can be reached at [email protected].











