![The 2017 4th of July Supply Chain [Infographic]](https://fronetics.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/4th-of-july.jpg)
by Fronetics | Jun 27, 2017 | Big Data, Blog, Current Events, Data/Analytics, Logistics, Supply Chain
U.S. Consumers plan to spend a whopping $7.1 billion on cookouts for 4th of July celebrations.
The National Retail Federation reports that 219 million Americans plan to celebrate the 241st Independence Day. Two-thirds plan to attend a cookout, barbecue, or picnic, spending an average of $73.42 per household on food items, up from last year’s $71.34. That’s a lot of hot dogs!
And what’s a Fourth of July celebration without fireworks? 44% of Americans plan to attend a fireworks show or community celebration. The U.S. will use approximately 285.3 million pounds of fireworks, totaling $1.09 billion dollars. More than 15,000 firework displays will glitter the skies to mark the special occasion.
Recognized as the nation’s largest Independence Day celebration, the Macy’s 4th of July Fireworks display attracts more than 3 million spectators live and over 10 million TV viewers. The firework display in Washington, D.C., comes in second with over 700,000 viewers from the nation’s capital.
And due to a number of factors — including strong employment and the low price of gasoline — a record number of people will travel out of town this year to celebrate the holiday. NRF estimates 32.9 million, while AAA estimates it will be closer to 44.2 million travelers.
At Fronetics, we wish you and your family a safe and fun Fourth of July celebration. Here are a few more fun facts to get you into the patriotic spirit.
A 2017 4th of July Infographic for the Supply Chain

(Made with Canva)
Related posts:

by Fronetics | Jun 7, 2017 | Blog, Content Marketing, Data/Analytics, Marketing, Social Media
Building brand awareness is one of the key benefits of content marketing, but it’s notoriously difficult to measure. Until now.
Content marketing is a long-term solution through which a business establishes a relationship with and earns the trust of target customers. It’s called building brand awareness. Drawing the public’s attention to — and heightening their knowledge of — your business ultimately generates leads that turn into sales, after all, which is the end marketing objective.
Let’s be honest: This doesn’t happen overnight. And it’s often difficult to quantify (as opposed to a vanity metric, such as website visits). But that’s not a reason to throw in the towel. There are ways to measure the work that you’re putting into your content marketing program. And, more specifically, there are ways to measure brand awareness.
4 metrics that indicate you’re building brand awareness
1) Social media reach
The reach of your social content has a direct impact on your brand awareness. The larger the reach, the larger the potential audience.
Twitter originally had an internal tool that tracked how many times a tweet had been shared, but stopped supporting this data back in 2015. So where do you go to track your social media reach?
Sharedcount is a free online tool that allows you to track the number of times a piece of content has been shared on social media, including Facebook, LinkedIn and Google. Sharedcount is an easy way to get basic information about your social reach, so you can spend less time tracking tweets and more time producing your content.
2) Brand mentions
There’s a great deal of value to be gained from monitoring discussions about your brand online. Tracking brand mentions can lead to honest feedback and objective insight from potential leads.
There are several options you can use to track brand mentions. We prefer the ease of Google Alerts, which allows you to easily set up a custom alert, or Hootsuite, where you can track brand mentions, as well as specific keywords and phrases, across all of your social media feeds.
3) Blog shares
By adding a share bar to your blog posts, you make it easy for readers to share your blog content on social networks, spreading awareness about your content and your brand through the amplifying effect of social media.
These share bars are easy to set up and even easier to monitor. By measuring your average number of shares per blog, you can track what content your users are drawn to and what pieces fall flat.
4) Search volume
One of the main sources of traffic for most websites is through simple searches. If people are searching for your company or products, that’s a pretty solid indication that they are aware of your brand.
Using online tools, such as Google Adwords or Moz, you can track the searches for your products, blogs, social media platforms, and any other variation that you find useful. These tools are free, easy to use, and perfect for determining if your company is popping up when customers are searching.
Content marketing takes time, but there are hints along the way that your efforts are working. Using these tools to measure brand awareness offers clues that customers are finding your company in their search efforts. If the needle is not moving in a positive direction, always adjust your strategy to until you find what works for your business.
Related posts:


by Fronetics | May 31, 2017 | Blog, Content Marketing, Data/Analytics, Marketing, Social Media
Analyzing the right metrics is crucial to determining whether you are achieving content marketing ROI.
We all want to see the fruits of our labors. Whether launching a product or a new social media campaign, we look for instantaneous numbers that will affirm we made the right choices. But here’s the problem: Not all metrics are created equal. Content marketing ROI is harder to confirm than checking a few quick numbers.
A spike in homepage hits may be the result of your marketing efforts, or it may be because of ghost spam. (Or, both.) Regardless, more visits do not necessarily correlate to increased revenue — just more visits. Even so, 83% of B2B enterprise companies (over 1,000 employees) use web traffic as their main metric for measuring content marketing ROI.
The number of email subscribers is another common success metric. But, again, having 100,000 email subscribers means nothing if only 0.001% are opening them. You actually could be losing money in terms of resources allocated if the emails aren’t helping drive sales. That’s why it is crucial to focus on your company’s return on investment (ROI). You could waste hours reviewing a hundred different analytics that tell you nothing about how revenue was affected by a particular effort.
Know where to allocate resources
Lean-startup pioneer Eric Reis said, “The only metrics that entrepreneurs should invest energy in collecting are those that help them make decisions.” In other words, measure the things that will tell you if an effort was profitable so you know where to put your time and money.
ROI can help you determine whether it was worth spending your resources in a particular way. This is extremely useful on platforms like blogs and social media, where things are constantly changing. Using ROI as a litmus test, you can keep experimenting and making sure you’re using these tools effectively.
According to our Social Media Use Report, 81% of respondents wanted a tracking and measuring tool to prove their ROI. Your resources are limited, so it’s crucial to evaluate your efforts with meaningful numbers that illustrate their affect on your bottom line.
So what are they best metrics to use? Here are three of our favorite tools.
3 tools for measuring content marketing ROI
1) Built-in Social Media Analytics Tools
Most social media platforms have their very own built-in tools that give you detailed information about engagement with your content. Even better, most of these tools are free. Twitter Analytics, Facebook Insight, and YouTube Analytics are just a few examples of tools you can use to measure exposure and engagement with your followers. This priceless information will help you gain a better understanding of your followers and the content they are drawn to.
2) Hootsuite
Hootsuite promotes smarter, data-driven social media marketing decisions backed by real-time analytics that allow you to spot trends as they develop and drill down for insights on how your social content is performing. It takes all your top social media platforms (Twitter, Facebook, YouTube, LinkedIn) and combines them into one application for full-scope results.
3) HubSpot
Measuring ROI through HubSpot is both accurate and convenient. HubSpot sends you weekly updates on your campaign performance and allows you to pull any reports of your own. Standard analysis includes: visits, leads, percentage changes, submissions, bounce rate, downloads, and much, much more. HubSpot Marketing Analytics can identify blog articles, landing pages, emails, and social media posts that perform well in terms of specific keywords.
Calculating ROI might take some time — both in the few extra minutes to do the math and the amount of time that needs to pass before all the data is available — but that number will be invaluable to you.
Let us help you get started. We’ve created a monthly marketing reporting template just for you. This template tracks your marketing metrics and generates graphs you can use in reporting and presentations. Click the button below to get the template (an Excel document) now.

Related posts:


by Fronetics | Mar 23, 2017 | Big Data, Blog, Current Events, Data/Analytics, Internet of Things, Logistics, Manufacturing & Distribution, Strategy, Supply Chain, Talent, Warehousing & Materials Handling
Our series by MBA students and graduates at Peter T. Paul College of Business and Economics highlights some of the most pressing issues in supply chain management today.
A few years ago, the Wall Street Journal called supply chain management the “hot new MBA.” Many universities have been introducing related degree programs, majors, and concentrations in response to a growing demand for new hires with supply chain expertise. Graduates of these programs are heavily recruited by employers, which is helping to attract ambitious, young talent to the industry.
Fronetics had the opportunity to collaborate with some of these rising stars by inviting MBA students from the University of New Hampshire Peter T. Paul College of Business and Economics to author guest posts on our blog. They covered a variety of pertinent topics, from the Internet of Things and Big Data to pet food and Chipotle. Their pieces are summarized below.
In the coming weeks, we’ll be partnering with another MBA class at UNH to author a second series of posts covering some of the most pressing issues in supply chain management today. Make sure you receive our blog e-newsletter (sign up to the right) or follow us on social media so that you don’t miss out.
Steve Mondazzi writes about how the Internet of Things is now being used to improve factory workflow, increase material tracking, and optimize distribution to maximize revenues. Everything from turning lights on and off to security systems can be controlled from your smartphone, and that technology is moving to the manufacturing industry. Mondazzi examines Mark Morely’s theory that the IoT will impact the industry in three main ways: pervasive visibility, proactive replenishment, and predictive maintenance. He also explores hurdles to implementation — such middleware and a common protocol for businesses regarding IoT. Read article
Mikayla Cadoret focuses on the barriers to entry in the pet food industry. New brands have three options: manufacture product themselves, choose a co-packer who uses a private label, or choose a co-packer who will manufacture the food to the specifications of the brand. She discusses the challenges of those choices as well as high-profiles recalls resulting from co-packer error. She recommends strategies that companies implement to keep tabs on co-packers’ sourcing and manufacturing. Read article
Nicole Brooks explores Amazon’s mission to be earth’s most consumer-centric company. The e-commerce giant not only offers low prices, it also exceeds consumer expectations and shifts industry standards with benefits like same-day shipping. Brooks examines Amazon’s biggest technological assets, and looks forward to up-and-coming innovations like Kiva robots in warehouses, drones, Prime Air, and Amazon Business. Read article
Corey Ducharme discusses the traditional four-step problem-solving method and how it isn’t effective in solving needle-in-a-haystack issues resulting from limited business resources. Six sigma can address these issue with its six-step process. With the addition of an analysis phase, solutions become more effective, leading to better results and higher revenue for businesses. Read article
David Chadwick explores whether advances in radio-frequency-identification technology (RFID) will render humans obsolete in the supply chain. RFID could dramatically improve efficiency and accuracy in warehouses by reducing the need for human interaction. But it is uncertain to what degree this technology will be implemented in all aspects of supply chain management. Read article
Dario Cavegn discusses how increasing size and complexity of global supply chains open them up to increased risk. Supply chain disruptions can vary from insignificant to extremely threatening. But regardless of disruption size, supply chains can remain resilient with a business continuity plan, which acts as a road map to continue operations during or after a disruption. Cavegn outlines the development process from analysis to feedback. Read article
Josh Hutchins explores the limitations of big data. The real value lies in the analytics applied to the data. As an example, Solid Gold Bomb drove its prospering t-shirt business into the ground from an oversight and misapplication of data. Hutchins concludes that companies must have an intimate understanding of big data applications to avoid a similar fate. Read article
Michael Hickey discusses third-party logistics providers as a resource for a company’s operations arm. 3PLs offer an outsourcing opportunity for order fulfillment, inventory and warehouse management, as well as transportation of finished goods. But businesses should ask themselves these questions when determining whether a 3PL is a good fit for their needs. Read article
Sarah Hebert discusses Chipotle’s high-profile pork-supplier conundrum. The chain cut their pork supply by a third due to a supplier’s violation of their animal welfare standards. While this affected sales by 7-8%, Chipotle embraced the situation as a strategic PR opportunity. But behind the scenes, the company was scrambling to address long-term supply concerns associated with its rapid growth. Hebert asks, “At what point do you scale back the growth for the sake of maintaining brand integrity?” Read article
Connor Harrison discusses GM’s recall of 2.6 million vehicles. The company’s faulty ignition switches were linked to 13 deaths and 31 front-end collisions, but the company managed to contain the crisis. Harrison examines the root causes of the issue, including faulty ignition switches from GM’s supplier Delphi, a strained business relationship, and legal complications. Read article
Related posts:
![The State of Supply Chains: The Supply Chain Has Gone Digital [Infographic]](https://fronetics.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/virtual-reality.jpg)
by Jennifer Hart Yim | Jan 23, 2017 | Big Data, Blog, Data/Analytics, Logistics, Strategy, Supply Chain
2016 was the year of the digital supply chain — here’s a look at how things changed.
This guest post comes to us from Adam Robinson, director of marketing for Cerasis, a top freight logistics company and truckload freight broker.
2016 marched onward with a drive to improve the use of digital technology throughout the supply chain. In our first supply chain trends post, we surmised the previous year’s trends would continue. However, this prediction proved to only touch on how important the digital supply chain would become.
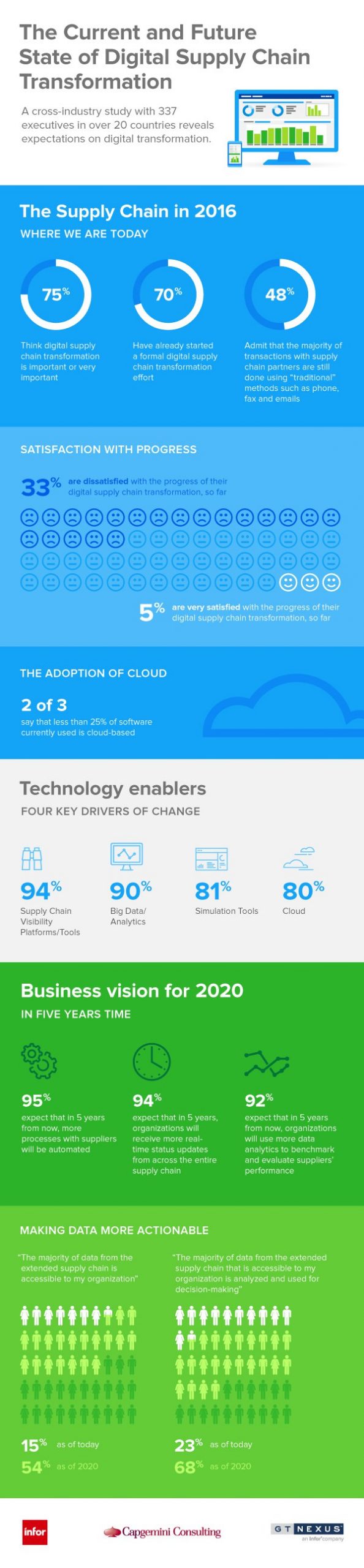
Within four months, the digital transformation had already reached most supply chain organizations. Per GT Nexus, 75% of executives surveyed recognized the digital supply chain as an important factor for the next five years. Meanwhile, 70% have also started processes to implement digital supply chain technologies throughout their companies.
Unfortunately, many supply chain entities continue to hope for a better tomorrow. In other words, the digital supply chain transformation has only been rated as very satisfying for 5% of respondents. In addition, just less than half (48%) of respondents report continued use of traditional technologies exclusively, which include the following:
- Fax machines
- Manual order entry and review
- Land-line phones, not voice over internet protocol (VoIP), which reduces overall costs and downtime
- Email, although beneficial, is susceptible to internet connectivity issues, security breaches and other problems
- Chaotic picking protocols
This infographic, created by GT Nexus, also shows other ways the digital supply chain evolved in 2016.
(Made with Canva)
Essentially, the digital supply chain is essential to gaining and maintaining competitive advantage. Digital technologies, reports Richard Howells of Forbes, including Big Data, analytics, the Internet of Things, social media, and point-of-sale reporting, enable business to know more about consumer needs and wants than ever before. Consequently, they can more accurately respond to changes in product demand across large distances and within infinitesimally small time frames.
Supply chain execs retained fundamentals throughout change.
Innovation is the driving force behind change and improvement in the modern world. Supply chains must evolve to meet an increasing number of omnichannel sales, and technologies must be integrated within existing systems to reach maximum efficiency and productive value.
As explained by Grant Marshbank of VSC Solutions, “The rate of change is not going to slow down. Technology will only delivery […] if it’s implemented with strategy and operations that adhere to best practices.”
Marshbank’s words highlighted the need to focus on fundamental concepts while responding to changes and improvements in the supply chain. For example, an optimized supply chain is good, but it opens more opportunities for errors. Simply putting all an organization’s proverbial eggs into one basket may be risky if appropriate auditing and review measures are not undertaken to ensure continued compliance and accuracy in all orders.
Change is a necessity for businesses, including the supply chain, to grow and expand. Yet many destructive forces can severely undermine a company’s progress. Bad weather, poor hiring practices or inefficient maintenance of consumers’ financial data can decimate a company. However, the response to hindrances in 2016 continued to showcase the importance of fundamental concepts, asserts Ryder, which include the following:
- Continually seeking the fastest, most cost-effective means of transporting products to consumers, including enhanced delivery optins.
- Expansion of global footprint while adhering to local, state, federal and international requirements
- Keeping companies accountable and focused on giving back to their domestic partners through reshoring or nearshoring
- Working with more outside agencies, also highlighted by Samantha Carr of Business 2 Community, including crowd-sourced logistics, warehouse optimization and outsourcing, and greater use of cloud-computing
Augmented reality found its place among consumers.
Augmented reality sounded amazing and far-fetched early in 2016, but the year has shown it to be one of the most successful product in existence. There tends to be more acceptance of technologies in the workplace once consumers can identify how they work.
For example, new hires are likely to pick up tablet-based systems more easily since they have been using them recreationally for some time. Essentially, the virtual-reality (VR), which is the precursor to augmented reality, hype of the 2016 Christmas shopping season is making more people excited about this new way to “see the world.”
While the VR hype may seem like it only emerged for Christmas, think about one of the hottest games of 2016, Pokémon Go! This app was built on augmented reality, combining the digital and physical worlds into one interactive environment. This technology, reports JOC.com, will be a key to practically eliminate extensive training courses and repair time requirements throughout the supply chain.
Ultimately, it translates into greater use of augmented reality in supply chains, which is growing by 100% annually, reports Barcoding Incorporated.
What’s next?
Clearly, technology dominated the conversation for 2016, but there are also changes in how supply chains operate that require a more in-depth discussion as well. In the next post of this series, we discuss the impact of artificial intelligence, agile processes and procurement expansion on the supply chain of 2016.
Related posts:
by Fronetics | Jan 19, 2017 | Blog, Content Marketing, Data/Analytics, Marketing, Social Media, Strategy
The chances are that your company is not tweeting as often as it should.
Each second around 6,000 tweets are tweeted. Each minute over 350,000 tweets are tweeted. The median lifespan of each of these tweets is just 18 minutes. After 18 minutes of being live, the chance of someone seeing your tweet is very low. The chance of someone interacting with that tweet — even lower.
Given the large volume of tweets and the short lifespan of each tweet, how often should you tweet?
To get the most value out of each tweet, tweet around five times each day. To get the most value out of your company’s Twitter presence as a whole, tweet up to 30 times per day.
At Fronetics, we recommend focusing on getting the most value out of your company’s twitter presence as opposed to getting the most value out of each tweet.
When developing your Twitter strategy, here are a few things to keep in mind:
Timing is everything.
Identify the time of day most of your followers are active and what time of day your tweets receive the highest level of engagement. Followerwonk and Tweriod are two tools you can use to conduct this analysis. Rival IQ takes the analysis one step further and shows you when your competitors are tweeting and when they are realizing their highest level of engagement.
It is important to conduct this analysis on a regular basis and to adjust your strategy accordingly.
Be relevant. Be strategic.
Every single tweet you send should be relevant and should fit within your strategic goals and objectives.
Don’t be annoying.
Tweeting when your followers are active and when you have the highest levels of engagement is important, but don’t go overboard. For example, if you learn that 10 a.m. and 2 p.m. are the best times of day for your company to tweet, do not schedule all 30 of your tweets to go live at those times.
Be creative.
Don’t tweet the same tweet over and over and over again. It’s ok to share the same article a few times, but change up the image and/or the tweet to make it fresh.
Be visual.
Tweets with images get more engagement than tweets without images. Analysis by Buffer found that tweets with images receive:
- 150% more retweets
- 89% more favorites
- 18% more clicks
Be realistic.
Determine what you can realistically do on a consistent basis. If you can only commit to tweeting 5 times per day, stick with that. It is better to have strategy that you can execute than to have a strategy that cannot realistically be executed.
Finally, remember you don’t need to go it alone. Tools such as Buffer, HootSuite, Sprout Social, and HubSpot allow you to schedule tweets. Scheduling tweets makes it easier to tweet more often so that you can realize the value of a Twitter strategy.
Related posts:
![The 2017 4th of July Supply Chain [Infographic]](https://fronetics.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/4th-of-july.jpg)








![The State of Supply Chains: The Supply Chain Has Gone Digital [Infographic]](https://fronetics.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/virtual-reality.jpg)

